Ultrasound Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) Based on the Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) to Distinguish Benign from Malignant Thyroid Nodules and the Diagnostic Performance of Radiologists with Different Diagnostic Experience
- PMID: 31929498
- PMCID: PMC6977643
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.918452
Ultrasound Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) Based on the Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) to Distinguish Benign from Malignant Thyroid Nodules and the Diagnostic Performance of Radiologists with Different Diagnostic Experience
Abstract
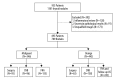
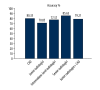
<strong>BACKGROUND</strong> The diagnosis of thyroid cancer and distinguishing benign from malignant thyroid nodules by junior radiologists can be challenging. This study aimed to develop a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system based on the Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) to distinguish benign from malignant thyroid nodules by analyzing ultrasound images to improve the diagnostic performance of junior radiologists. <strong>MATERIAL AND METHODS</strong> A modified TI-RADS based on a convolutional neural network (CNN) was used to develop the CAD system. This retrospective study reviewed 789 thyroid nodules from 695 patients and included radiologists with different diagnostic experience. Five study groups included the CAD group, the junior radiologist group, the intermediate-level radiologist group, the senior radiologist group, and the group in which the junior radiologist used the CAD system. The ultrasound findings were reviewed and compared with the histopathology diagnosis. <strong>RESULTS</strong> The CAD system for the diagnosis of thyroid cancer showed an accuracy of 80.35%, a sensitivity of 80.64%, a specificity of 80.13%, a positive predictive value (PPV) of 76.02%, a negative predictive value (NPV) of 84.12%, and an area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) of 0.87. The accuracy of the junior radiologists in diagnosing thyroid cancer using CAD was similar to that of intermediate-level radiologists (79.21% vs. 77.57%; P=0.427). <strong>CONCLUSIONS</strong> The use of ultrasound CAD based on the TI-RADS showed potential for distinguishing between benign and malignant thyroid nodules and improved the diagnostic performance of junior radiologists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Investigating the diagnostic efficiency of a computer-aided diagnosis system for thyroid nodules in the context of Hashimoto's thyroiditis.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 5;12:941673. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.941673. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36686823 Free PMC article.
-
Computer-aided diagnosis system of thyroid nodules ultrasonography: Diagnostic performance difference between computer-aided diagnosis and 111 radiologists.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jun 5;99(23):e20634. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020634. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32502044 Free PMC article.
-
The value of the Demetics ultrasound-assisted diagnosis system in the differential diagnosis of benign from malignant thyroid nodules and analysis of the influencing factors.Eur Radiol. 2021 Oct;31(10):7936-7944. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07884-z. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33856523
-
Effectiveness evaluation of computer-aided diagnosis system for the diagnosis of thyroid nodules on ultrasound: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Aug;98(32):e16379. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016379. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31393347 Free PMC article.
-
Update on ACR TI-RADS: Successes, Challenges, and Future Directions, From the AJR Special Series on Radiology Reporting and Data Systems.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021 Mar;216(3):570-578. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.24608. Epub 2021 Jan 21. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021. PMID: 33112199 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic performance evaluation of different TI-RADS using ultrasound computer-aided diagnosis of thyroid nodules: An experience with adjusted settings.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 15;16(1):e0245617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245617. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33449958 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diagnostic value of a computer-assisted diagnosis system for the ultrasound features in thyroid nodules.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Nov 10;68:e220501. doi: 10.20945/2359-4292-2022-0501. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37948567 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosing thyroid nodules with atypia of undetermined significance/follicular lesion of undetermined significance cytology with the deep convolutional neural network.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 8;11(1):20048. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99622-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34625636 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Thyroid Field-A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 22;13(19):4740. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194740. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence for Personalized Medicine in Thyroid Cancer: Current Status and Future Perspectives.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 9;10:604051. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.604051. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33634025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2016;26:1–133. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brito JP, Morris JC, Montori VM. Thyroid cancer: Zealous imaging has increased detection and treatment of low risk tumours. BMJ. 2013;347:f4706. - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(4):271–89. - PubMed
-
- Grant EG, Tessler FN, Hoang JK, et al. Thyroid ultrasound reporting lexicon: White paper of the ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS) Committee. J Am Coll Radiol. 2015;12:1272–79. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

