Erythropoietin Alleviates Burn-induced Muscle Wasting
- PMID: 31929736
- PMCID: PMC6945565
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.38590
Erythropoietin Alleviates Burn-induced Muscle Wasting
Abstract
Background: Burn injury induces long-term skeletal muscle pathology. We hypothesized EPO could attenuate burn-induced muscle fiber atrophy. Methods: Rats were allocated into four groups: a sham burn group, an untreated burn group subjected to third degree hind paw burn, and two burn groups treated with weekly or daily EPO for four weeks. Gastrocnemius muscle was analyzed at four weeks post-burn. Results: EPO attenuated the reduction of mean myofiber cross-sectional area post-burn and the level of the protective effect was no significant difference between two EPO-treated groups (p=0.784). Furthermore, EPO decreased the expression of atrophy-related ubiquitin ligase, atrogin-1, which was up-regulated in response to burn. Compared to untreated burn rats, those receiving weekly or daily EPO groups had less cell apoptosis by TUNEL assay. EPO decreased the expression of cleaved caspase 3 (key factor in the caspase-dependent pathway) and apoptosis-inducing factor (implicated in the caspase-independent pathway) after burn. Furthermore, EPO alleviated connective tissue overproduction following burn via transforming growth factor beta 1-Smad2/3 pathway. Daily EPO group caused significant erythrocytosis compared with untreated burn group but not weekly EPO group. Conclusion: EPO therapy attenuated skeletal muscle apoptosis and fibrosis at four weeks post-burn. Weekly EPO may be a safe and effective option in muscle wasting post-burn.
Keywords: Apoptosis Inducing Factor; Burn injury; Erythropoietin; Muscle fiber atrophy; Transforming Growth Factor beta1.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

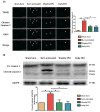
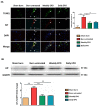



References
-
- Pereira C, Murphy K, Jeschke M, Herndon DN. Post burn muscle wasting and the effects of treatments. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology. 2005;37:1948–61. - PubMed
-
- Bolton CF. Sepsis and the systemic inflammatory response syndrome: neuromuscular manifestations. Critical care medicine. 1996;24:1408–16. - PubMed
-
- Chang DW, DeSanti L, Demling RH. Anticatabolic and anabolic strategies in critical illness: a review of current treatment modalities. Shock. 1998;10:155–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

