Innate Lymphoid Cells: Regulators of Gut Barrier Function and Immune Homeostasis
- PMID: 31930146
- PMCID: PMC6942837
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/2525984
Innate Lymphoid Cells: Regulators of Gut Barrier Function and Immune Homeostasis
Abstract
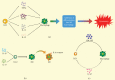
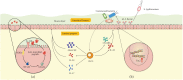
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), identified in the early years of this century as a new class of leukocyte family unlike the B or T lymphocytes, play a unique role bridging the innate and adaptive immune responses in mucosal immunity. Their origin, differentiation, and activation process and functions have caught global interest. Recently, accumulating evidence supports that ILCs are vital regulators for gastrointestinal mucosal homeostasis through interactions with other structural and stromal cells in gut epithelial barriers. This review will explore the functions of ILCs and other cells in maintaining gut homeostasis and feature the crosstalk between ILCs with other cells and potential pharmacotherapy targeting ILCs applicable in intestinal innate immunity.
Copyright © 2019 Hui Fan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Viggiano D., Ianiro G., Vanella G., et al. Gut barrier in health and disease: focus on childhood. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2015;19(6):1077–1085. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

