Synthesis of Ultrasmall Synthetic Melanin Nanoparticles by UV Irradiation in Acidic and Neutral Conditions
- PMID: 31930189
- PMCID: PMC6953903
- DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.9b00747
Synthesis of Ultrasmall Synthetic Melanin Nanoparticles by UV Irradiation in Acidic and Neutral Conditions
Abstract
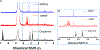
Synthetic melanin nanoparticles have value in metal chelation, photoprotection, and biocompatibility. Applications of these materials have been reported in optics, biomedicine, and electronics. However, precise size control has remained relatively difficult-especially for materials below 1000 nm. In this paper we describe the synthesis of ultrasmall synthetic nanoparticles with size of 9.4-31.4 nm in weakly acidic and neutral conditions via UV-irradiation. Size control of these particles was possible by varying the pH from 6.4-10.0. We then used UV-vis, FTIR, and nuclear magnetic resonance to investigate the mechanism of UV-induced polymerization. The data show that reactive oxygen species from UV irradiation oxidizes intermediates of the reaction and accelerates the formation of these synthetic melanin structures.
Keywords: UV irradiation; facile preparation; mechanism; melanin; polydopamine; synthesis; synthetic melanin nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
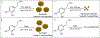

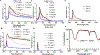
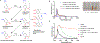
References
-
- Jiang Q; Luo Z; Men Y; Yang P; Peng H; Guo R; Tian Y; Pang Z; Yang W Red Blood Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Melanin Nanoparticles for Enhanced Photothermal Therapy. Biomaterials 2017, 143, 29–45. - PubMed
-
- Zhang R; Fan Q; Yang M; Cheng K; Lu X; Zhang L; Huang W; Cheng Z Engineering Melanin Nanoparticles as an Efficient Drug–Delivery System for Imaging-Guided Chemotherapy. Adv. Mater 2015, 27 (34), 5063–5069. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
