ADP-ribosylation: from molecular mechanisms to human disease
- PMID: 31930280
- PMCID: PMC7198025
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2019-0075
ADP-ribosylation: from molecular mechanisms to human disease
Abstract
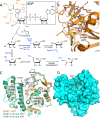
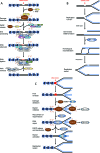
Post-translational modification of proteins by ADP-ribosylation, catalysed by poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) using NAD+ as a substrate, plays central roles in DNA damage signalling and repair, modulates a range of cellular signalling cascades and initiates programmed cell death by parthanatos. Here, we present mechanistic aspects of ADP-ribose modification, PARP activation and the cellular functions of ADP-ribose signalling, and discuss how this knowledge is uncovering therapeutic avenues for the treatment of increasingly prevalent human diseases such as cancer, ischaemic damage and neurodegeneration.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

