Intracellular Neutralization of Ricin Toxin by Single-domain Antibodies Targeting the Active Site
- PMID: 31931008
- PMCID: PMC7066583
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.01.006
Intracellular Neutralization of Ricin Toxin by Single-domain Antibodies Targeting the Active Site
Abstract
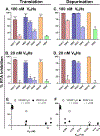
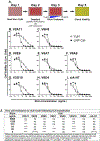
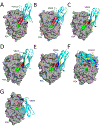
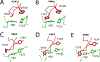
The extreme potency of the plant toxin, ricin, is due to its enzymatic subunit, RTA, which inactivates mammalian ribosomes with near-perfect efficiency. Here we characterized, at the functional and structural levels, seven alpaca single-domain antibodies (VHHs) previously reported to recognize epitopes in proximity to RTA's active site. Three of the VHHs, V2A11, V8E6, and V2G10, were potent inhibitors of RTA in vitro and protected Vero cells from ricin when expressed as intracellular antibodies ("intrabodies"). Crystal structure analysis revealed that the complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) elements of V2A11 and V8E6 penetrate RTA's active site and interact with key catalytic residues. V2G10, by contrast, sits atop the enzymatic pocket and occludes substrate accessibility. The other four VHHs also penetrated/occluded RTA's active site, but lacked sufficient binding affinities to outcompete RTA-ribosome interactions. Intracellular delivery of high-affinity, single-domain antibodies may offer a new avenue in the development of countermeasures against ricin toxin.toxin, antibody, structure, intracellular.
Keywords: Antibody; Intracellular; Structure; Toxin.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

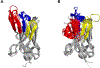
Similar articles
-
Single-Domain Antibodies for Intracellular Toxin Neutralization.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2446:469-487. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2075-5_24. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35157289
-
Structural Analysis of Toxin-Neutralizing, Single-Domain Antibodies that Bridge Ricin's A-B Subunit Interface.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jul 23;433(15):167086. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167086. Epub 2021 Jun 3. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34089718
-
A Biparatopic Intrabody Renders Vero Cells Impervious to Ricin Intoxication.Biochemistry. 2024 Oct 1;63(19):2391-2396. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00385. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 39297955
-
Immunity to ricin: fundamental insights into toxin-antibody interactions.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;357:209-41. doi: 10.1007/82_2011_193. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22113742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-based design of ricin inhibitors.Toxins (Basel). 2011 Oct;3(10):1233-48. doi: 10.3390/toxins3101233. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22069693 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The structural basis of Salmonella A2B5 toxin neutralization by antibodies targeting the glycan-receptor binding subunits.Cell Rep. 2021 Sep 7;36(10):109654. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109654. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34496256 Free PMC article.
-
A Monoclonal Antibody with a High Affinity for Ricin Isoforms D and E Provides Strong Protection against Ricin Poisoning.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Sep 24;16(10):412. doi: 10.3390/toxins16100412. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39453188 Free PMC article.
-
Current and future advances in fluorescence-based visualization of plant cell wall components and cell wall biosynthetic machineries.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021 Mar 29;14(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s13068-021-01922-0. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021. PMID: 33781321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Slaying SARS-CoV-2 One (Single-domain) Antibody at a Time.Trends Microbiol. 2021 Mar;29(3):195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.12.006. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Trends Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33446406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of typhoid toxin neutralization by antibodies targeting glycan receptor binding and nuclease subunits.iScience. 2021 Apr 20;24(5):102454. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102454. eCollection 2021 May 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34113815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sapoznikov A et al., Early disruption of the alveolar-capillary barrier in a ricin-induced ARDS mouse model: neutrophil-dependent and -independent impairment of junction proteins. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

