New Evidence and Insights on Dalbavancin and Wound Healing in a Mouse Model of Skin Infection
- PMID: 31932371
- PMCID: PMC7179315
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02062-19
New Evidence and Insights on Dalbavancin and Wound Healing in a Mouse Model of Skin Infection
Abstract
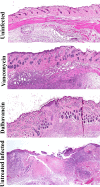
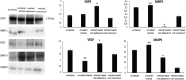
Dalbavancin is an effective antibiotic that is widely used to treat skin infection. Our aim was to determine the effect of dalbavancin administration on wound healing compared to that of vancomycin and to elucidate if epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1), MMP-9, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) could be involved in its therapeutic mechanism. A mouse model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) skin infection was established. Mice were treated daily with vancomycin (10 mg/kg) and weekly with dalbavancin at day 1 (20 mg/kg) and day 8 (10 mg/kg). After 14 days, wounds were excised, and bacterial counts were performed. Wound healing was assessed by histological and immunohistochemical staining, followed by protein extraction and immunoblotting. Our microbiological results confirmed that both dalbavancin and vancomycin are effective in reducing the bacterial load in wounds. The dalbavancin group showed a strong effect compared with infected untreated animals and the vancomycin-treated group. The wounds treated with dalbavancin showed robust epidermal coverage with reconstitution of the regular and keratinized epidermal lining and well-organized granulation tissue with numerous blood vessels, although slightly less than that in the uninfected group. While in the vancomycin-treated group the epithelium appeared, in general, still hypertrophic, the granulation tissue appeared even less organized. We observed elevated EGFR and VEGF expression in both treated groups, although it was higher in dalbavancin-treated mice. MMP-1 and MMP-9 were decreased in uninfected tissue and in both treated tissues compared with untreated infected wounds. This study showed faster healing with dalbavancin treatment that might be associated with higher EGFR and VEGF levels.
Keywords: EGFR; MMP-1; MMP-9; VEGF; dalbavancin; wound healing.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Russo A, Concia E, Cristini F, De Rosa FG, Esposito S, Menichetti F, Petrosillo N, Tumbarello M, Venditti M, Viale P, Viscoli C, Bassetti M. 2016. Current and future trends in antibiotic therapy of acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections. Clin Microbiol Infect 2:S27–S36. doi: 10.1016/S1198-743X(16)30095-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barlam TF, Cosgrove SE, Abbo LM, MacDougall C, Schuetz AN, Septimus EJ, Srinivasan A, Dellit TH, Falck-Ytter YT, Fishman NO, Hamilton CW, Jenkins TC, Lipsett PA, Malani PN, May LS, Moran GJ, Neuhauser MM, Newland JG, Ohl CA, Samore MH, Seo SK, Trivedi KK. 2016. Implementing an antibiotic stewardship program: guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Clin Infect Dis 62:e51–e77. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw118. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

