Hepatic hemangioma: What internists need to know
- PMID: 31933511
- PMCID: PMC6952297
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i1.11
Hepatic hemangioma: What internists need to know
Abstract
Hepatic hemangioma (HH) is the most common benign liver tumor and it is usually found incidentally during radiological studies. This tumor arises from a vascular malformation; however, the pathophysiology has not been clearly elucidated. Symptoms usually correlate with the size and location of the tumor. Less commonly the presence of a large HH may cause life-threatening conditions. The diagnosis can be established by the identification of HH hallmarks in several imaging studies. In patients that present with abdominal symptoms other etiologies should be excluded first before attributing HH as the cause. In asymptomatic patient's treatment is not required and follow up is usually reserved for HH of more than 5 cm. Symptomatic patients can be managed surgically or with other non-surgical modalities such as transcatheter arterial embolization or radiofrequency ablation. Enucleation surgery has shown to have fewer complications as compared to hepatectomy or other surgical techniques. Progression of the tumor is seen in less than 40%. Hormone stimulation may play a role in HH growth; however, there are no contraindications for hormonal therapy in patients with HH due to the lack of concrete evidence. When clinicians encounter this condition, they should discern between observation and surgical or non-surgical management based on the clinical presentation.
Keywords: Hepatic hemangioma; Liver; Liver masses; Vascular lesion.
©The Author(s) 2019. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declare no conflict of interest related to this publication.
Figures
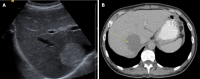
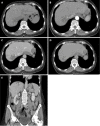
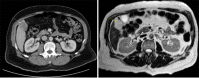
References
-
- Ishak KG, Rabin L. Benign tumors of the liver. Med Clin North Am. 1975;59:995–1013. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z, Tan H, Liu X, Sun Y. Extremely Giant Liver Hemangioma (50 cm) with Kasabach-Merritt Syndrome. J Gastrointest Surg. 2017;21:1748–1749. - PubMed
-
- Schumacker HB., Jr Hemangioma of the liver: discussion of symptomatology and report of patient treated by operation. Surgery. 1942;11:209–222.
-
- Reddy KR, Kligerman S, Levi J, Livingstone A, Molina E, Franceschi D, Badalamenti S, Jeffers L, Tzakis A, Schiff ER. Benign and solid tumors of the liver: relationship to sex, age, size of tumors, and outcome. Am Surg. 2001;67:173–178. - PubMed
-
- Hasan HY, Hinshaw JL, Borman EJ, Gegios A, Leverson G, Winslow ER. Assessing normal growth of hepatic hemangiomas during long-term follow-up. JAMA Surg. 2014;149:1266–1271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

