The expressions of autotaxin-lysophosphatidate signaling-related proteins in metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 31934128
- PMCID: PMC6949729
The expressions of autotaxin-lysophosphatidate signaling-related proteins in metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: We evaluated the expression of autotaxin-lysophosphatidate signaling-related proteins and the clinical implications for metastatic breast cancer.
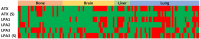
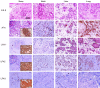
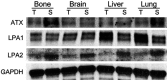
Methods: We constructed tissue microarrays (TMA) with 126 cases of metastatic breast cancer [31 (24.6%) bone metastases, 36 (28.6%) brain metastases, 11 (8.7%) liver metastases, and 48 (38.1%) lung metastasis], and we conducted immunohistochemical staining for the autotoxin-lysophosphatidate signaling-related proteins ATX, LPA1, LPA2, and LPA3.
Results: Stromal ATX (P = 0.006) and LPA1 (P < 0.001) were differently expressed according to their metastatic organ; stromal ATX showed high expression in bone metastasis, and LPA1 showed high expression in liver and lung metastases. Stromal ATX positivity was higher than others in luminal A type tumors (P = 0.035), and stromal LPA3 positivity was correlated with a high Ki-67 labeling index (LI) (P = 0.005). In univariate analysis, tumoral LPA3 negativity was correlated with shorter overall survival (OS) (P = 0.015) in metastatic breast cancer. When analyzed according to the metastatic sites, tumoral LPA3 negativity was correlated with shorter OS (P = 0.010) in lung metastasis, whereas stromal LPA3 negativity was correlated with shorter OS (P = 0.026) in brain metastasis. In multivariate Cox analysis, tumoral LPA3 negativity was an independent poor prognostic factor (HR = 2.311, 95% CI: 1.029-5.191, P = 0.043).
Conclusion: Among autotoxin-lysophosphatidate signaling-related proteins, stromal ATX was highly expressed in bone metastases, and LPA1 was highly expressed in liver and lung metastases. Tumoral LPA3 might be a prognostic factor in metastatic breast cancer.
Keywords: Autotaxin; breast cancer; lysophosphatidate receptor; metastasis.
IJCEP Copyright © 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of proteins related to autotaxin-lysophosphatidate signaling in thyroid tumors.J Transl Med. 2019 Aug 28;17(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-2028-7. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31455351 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Autotaxin⁻Lysophosphatidate Signaling-Related Proteins in Breast Cancer with Adipose Stroma.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 29;20(9):2102. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092102. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31035435 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific expression of amine oxidases in breast cancer metastases.Tumour Biol. 2018 May;40(5):1010428318776822. doi: 10.1177/1010428318776822. Tumour Biol. 2018. PMID: 29775160
-
The critical role and potential target of the autotaxin/lysophosphatidate axis in pancreatic cancer.Tumour Biol. 2017 Mar;39(3):1010428317694544. doi: 10.1177/1010428317694544. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28347252 Review.
-
The role and therapeutic potential of the autotaxin-lysophosphatidate signalling axis in breast cancer.Biochem J. 2014 Oct 1;463(1):157-65. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140680. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 25195735 Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity and Cancer Metastasis: Molecular and Translational Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 16;12(12):3798. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123798. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33339340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the therapeutic promise: exploring Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) signaling in malignant bone tumors for novel cancer treatments.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jun 28;23(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02196-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38943207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autotaxin: An Early Warning Biomarker for Acute-on-chronic Liver Failure.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2020 Sep 28;8(3):240-245. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00045. Epub 2020 Jul 21. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 33083245 Free PMC article.
-
M1 macrophage-derived exosomal microRNA-29c-3p suppresses aggressiveness of melanoma cells via ENPP2.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Sep 28;24(1):325. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03512-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39342305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jansen S, Stefan C, Creemers JW, Waelkens E, Van Eynde A, Stalmans W, Bollen M. Proteolytic maturation and activation of autotaxin (NPP2), a secreted metastasis-enhancing lysophospholipase D. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:3081–3089. - PubMed
-
- van Meeteren LA, Moolenaar WH. Regulation and biological activities of the autotaxin-LPA axis. Prog Lipid Res. 2007;46:145–160. - PubMed
-
- Choi JW, Herr DR, Noguchi K, Yung YC, Lee CW, Mutoh T, Lin ME, Teo ST, Park KE, Mosley AN, Chun J. LPA receptors: subtypes and biological actions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;50:157–186. - PubMed
-
- Houben AJ, Moolenaar WH. Autotaxin and LPA receptor signaling in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011;30:557–565. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
