Treatment with Intramuscular Levothyroxine in Refractory Hypothyroidism
- PMID: 31934558
- PMCID: PMC6944946
- DOI: 10.1159/000503324
Treatment with Intramuscular Levothyroxine in Refractory Hypothyroidism
Abstract
Introduction: Orally and daily levothyroxine (LT4) is the treatment of choice for hypothyroidism. In the majority of cases, the lack of effectiveness by this way may be due to poor adherence; however, gastrointestinal malabsorption may explain more cases of thyroxine refractoriness than previously reputed, due to the number of occult forms of these disorders.
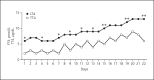
Case presentation: A 55-year-old white man with a diagnosis of low risk of recurrence of follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma was treated with total thyroidectomy, 30 mCi iodine 131, and oral LT4. A year before he presented a gastric adenocarcinoma that required a partial gastrectomy. He evolved with multiple episodes of intestinal subocclusion that had to be treated with enterectomy in the first instance, then digestive rest and total parenteral nutrition. In spite of having made increases in oral LT4 dose (3 µg/kg), the patient persisted with a thyroid-stimulating hormone level >100 mIU/L. For this reason, we decided to administer intramuscular LT4.
Conclusion: Since there are no guidelines or consensus of intramuscular LT4 use, our experience and how we decided the dose and way of administration are presented in this article to contribute to future cases.
Keywords: Intramuscular levothyroxine; Levothyroxine therapy; Refractory hypothyroidism.
Copyright © 2019 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Química Montpellier Laboratory provides LT4 only for parenteral use because this compound is not for sale for patients in Argentina. The laboratory delivers it to the Buenos Aires British Hospital pharmacy free of charge and given the clinical condition of the patient, without requesting any kind of compensation from the attending physicians.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Levothyroxine liquid oral substitution as an alternative treatment for refractory hypothyroidism due to gastrointestinal malabsorption: A case report.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2023 Nov 2;11:2050313X231209229. doi: 10.1177/2050313X231209229. eCollection 2023. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37927364 Free PMC article.
-
Levothyroxine malabsorption following sleeve gastrectomy.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2025 Jan 27;2025(1):e240115. doi: 10.1530/EDM-24-0115. Print 2025 Jan 1. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39868565 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of subcutaneous Levothyroxine in a case of refractory hypothyroidism: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jul 1;101(26):e29690. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029690. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35777000 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative routes of levothyroxine administration for hypothyroidism.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2020 Oct;27(5):318-322. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000558. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2020. PMID: 32740045 Review.
-
Levothyroxine Therapy in Thyrodectomized Patients.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jan 29;11:626268. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.626268. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33584551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Approach to adult patients with primary hypothyroidism in some special situations: a position statement from the Thyroid Department of the Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism (SBEM).Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Nov 17;66(6):871-882. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000545. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 36394484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lips DJ, van Reisen MT, Voigt V, Venekamp W. Diagnosis and treatment of levothyroxine pseudomalabsorption. Neth J Med. 2004 Apr;62((4)):114–8. - PubMed
-
- Virili C, Bassotti G, Santaguida MG, Iuorio R, Del Duca SC, Mercuri V, et al. Atypical celiac disease as cause of increased need for thyroxine: a systematic study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Mar;97((3)):E419–22. - PubMed
-
- Cellini M, Santaguida MG, Gatto I, Virili C, Del Duca SC, Brusca N, et al. Systematic appraisal of lactose intolerance as cause of increased need for oral thyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Aug;99((8)):E1454–8. - PubMed
-
- Travis LB, Curtis RE, Storm H, Hall P, Holowaty E, Van Leeuwen FE, et al. Risk of second malignant neoplasms among long-term survivors of testicular cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997 Oct;89((19)):1429–39. - PubMed