Myosin II Reactivation and Cytoskeletal Remodeling as a Hallmark and a Vulnerability in Melanoma Therapy Resistance
- PMID: 31935375
- PMCID: PMC6958528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.12.003
Myosin II Reactivation and Cytoskeletal Remodeling as a Hallmark and a Vulnerability in Melanoma Therapy Resistance
Abstract
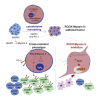
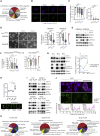
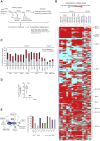
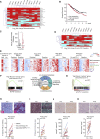
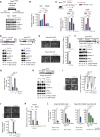
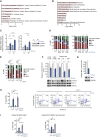
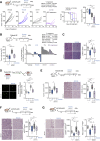
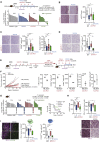
Despite substantial clinical benefit of targeted and immune checkpoint blockade-based therapies in melanoma, resistance inevitably develops. We show cytoskeletal remodeling and changes in expression and activity of ROCK-myosin II pathway during acquisition of resistance to MAPK inhibitors. MAPK regulates myosin II activity, but after initial therapy response, drug-resistant clones restore myosin II activity to increase survival. High ROCK-myosin II activity correlates with aggressiveness, identifying targeted therapy- and immunotherapy-resistant melanomas. Survival of resistant cells is myosin II dependent, regardless of the therapy. ROCK-myosin II ablation specifically kills resistant cells via intrinsic lethal reactive oxygen species and unresolved DNA damage and limits extrinsic myeloid and lymphoid immunosuppression. Efficacy of targeted therapies and immunotherapies can be improved by combination with ROCK inhibitors.
Keywords: MAPK; Rho-kinase; cytoskeletal remodeling; immunotherapy; melanoma therapy resistance; myosin II; phosphoproteomics and transcriptomics; regulatory T cells; transcriptional rewiring; tumor-promoting macrophages.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander S., Friedl P. Cancer invasion and resistance: interconnected processes of disease progression and therapy failure. Trends Mol. Med. 2012;18:13–26. - PubMed
-
- Arozarena I., Sanchez-Laorden B., Packer L., Hidalgo-Carcedo C., Hayward R., Viros A., Sahai E., Marais R. Oncogenic BRAF induces melanoma cell invasion by downregulating the cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE5A. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:45–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- C33043/A12065/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- FC001112/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- C107/A104339/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C33043/A24478/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- FC001112/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/L023091/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 24478/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- FC001112/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C107/A10433/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C10355/A15587/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 23783/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C30122/A15774/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C30122/A11527/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

