Curcumin as a Therapeutic Option in Retinal Diseases
- PMID: 31935797
- PMCID: PMC7023263
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9010048
Curcumin as a Therapeutic Option in Retinal Diseases
Abstract
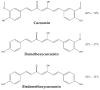
The retina is subjected to oxidative stress due to its high vascularization, long time light exposition and a high density of mitochondria. Oxidative stress can lead to pathological processes, like cell apoptosis, angiogenesis and inflammation ending in retinal pathologies. Curcumin, a major bioactive component obtained from the spice turmeric (Curcuma longa) rhizome has been used for centuries in Asian countries for cooking and for curing all kinds of diseases like dysentery, chest congestion and pain in general, due to its antioxidant effects. Curcumin prevents the formation of reactive oxygen species and so it is a good protective agent. Curcumin has shown also anti-inflammatory, and antitumor properties. Curcumin is a natural product, which can be a therapeutic option in a variety of retinal diseases due to its pleiotropic properties. Some drawbacks are its poor solubility, bioavailability and lack of stability at physiological conditions; which have been shown in curcumin skeptical publications. In this review, we provide some lights and shadows on curcumin administration on the major retinal pathologies.
Keywords: curcumin; oxidative stress; retina; retinal diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic potential of curcumin in major retinal pathologies.Int Ophthalmol. 2019 Mar;39(3):725-734. doi: 10.1007/s10792-018-0845-y. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Int Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 29404861 Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory role of curcumin in retinal disorders (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jul;22(1):790. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10222. Epub 2021 May 21. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34055089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of 12/15 lipoxygenase by curcumin and an extract from Curcuma longa L.Ceska Slov Farm. 2014 Feb;63(1):26-31. Ceska Slov Farm. 2014. PMID: 24568335
-
Curcumin, an active component of turmeric (Curcuma longa), and its effects on health.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Sep 2;57(13):2889-2895. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2015.1077195. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017. PMID: 26528921 Review.
-
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;595:105-25. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-46401-5_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17569207 Review.
Cited by
-
Properties, Extraction Methods, and Delivery Systems for Curcumin as a Natural Source of Beneficial Health Effects.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Jul 3;56(7):336. doi: 10.3390/medicina56070336. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32635279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fe-curcumin nanozyme-mediated immunosuppression and anti-inflammation in experimental autoimmune uveitis.Biomater Res. 2023 Dec 12;27(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s40824-023-00451-1. Biomater Res. 2023. PMID: 38087367 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into Dose-Dependent Effects of Curcumin on ARPE-19 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 25;23(23):14771. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314771. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499098 Free PMC article.
-
Polymyxins-Curcumin Combination Antimicrobial Therapy: Safety Implications and Efficacy for Infection Treatment.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jun 9;9(6):506. doi: 10.3390/antiox9060506. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32526966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights on Dietary Polyphenols for the Management of Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 8;12(6):1237. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061237. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnal E., Johnsen-Soriano S., Lopez-Malo D., Perez-Pastor G., Vidal-Gil L., Morillas N., Sancho-Pelluz J., Romero F., Barcia J. Docosahexaenoic Acid Protects against High Glucose-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. React. Oxyg. Species. 2016;2:298–307. doi: 10.20455/ros.2016.843. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources