Herba H outtuyniae Extract Benefits Hyperlipidemic Mice via Activation of the AMPK/PGC-1α/Nrf2 Cascade
- PMID: 31936037
- PMCID: PMC7019422
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12010164
Herba H outtuyniae Extract Benefits Hyperlipidemic Mice via Activation of the AMPK/PGC-1α/Nrf2 Cascade
Abstract
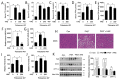
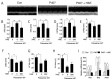
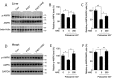
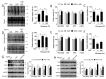
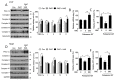
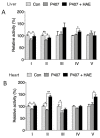
Hyperlipidemia is associated with metabolic disorders, but the detailed mechanisms and related interventions remain largely unclear. As a functional food in Asian diets, Herba houttuyniae has been reported to have beneficial effects on health. The present research was to investigate the protective effects of Herba houttuyniae aqueous extract (HAE) on hyperlipidemia-induced liver and heart impairments and its potential mechanisms. Male C57BL/6J mice were administered with 200 or 400 mg/kg/day HAE for 9 days, followed by intraperitoneal injection with 0.5 g/kg poloxamer 407 to induce acute hyperlipidemia. HAE treatment significantly attenuated excessive serum lipids and tissue damage markers, prevented hepatic lipid deposition, improved cardiac remodeling, and ameliorated hepatic and cardiac oxidative stress induced by hyperlipidemia. More importantly, NF-E2 related factor (Nrf2)-mediated antioxidant and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1α)-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis pathways as well as mitochondrial complex activities were downregulated in the hyperlipidemic mouse livers and hearts, which may be attributable to the loss of adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity: all of these changes were reversed by HAE supplementation. Our findings link the AMPK/PGC-1α/Nrf2 cascade to hyperlipidemia-induced liver and heart impairments and demonstrate the protective effect of HAE as an AMPK activator in the prevention of hyperlipidemia-related diseases.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase; Herba houttuyniae; hyperlipidemia; mitochondrial biogenesis; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
α-Ketoglutarate prevents hyperlipidemia-induced fatty liver mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress by activating the AMPK-pgc-1α/Nrf2 pathway.Redox Biol. 2024 Aug;74:103230. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103230. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38875959 Free PMC article.
-
Hawthorn total flavonoids ameliorate hyperlipidemia through AMPK/SREBP1-c and PPARα/PGC-1α/CPT-1A pathway activation and gut microbiota modulation.J Sci Food Agric. 2025 Jun;105(8):4326-4337. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.14188. Epub 2025 Feb 27. J Sci Food Agric. 2025. PMID: 40013442
-
Gui Qi Zhuang Jin Decoction ameliorates mitochondrial dysfunction in sarcopenia mice via AMPK/PGC-1α/Nrf2 axis revealed by a metabolomics approach.Phytomedicine. 2024 Oct;133:155908. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155908. Epub 2024 Jul 28. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39094439
-
Adaptation of Skeletal Muscles to Contractile Activity of Varying Duration and Intensity: The Role of PGC-1α.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2018 Jun;83(6):613-628. doi: 10.1134/S0006297918060019. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2018. PMID: 30195320 Review.
-
Dysregulated Autophagy Mediates Sarcopenic Obesity and Its Complications via AMPK and PGC1α Signaling Pathways: Potential Involvement of Gut Dysbiosis as a Pathological Link.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 19;21(18):6887. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186887. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32961822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperoside and Quercitrin in Houttuynia cordata Extract Attenuate UVB-Induced Human Keratinocyte Cell Damage and Oxidative Stress via Modulation of MAPKs and Akt Signaling Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 24;11(2):221. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020221. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204104 Free PMC article.
-
α-Ketoglutarate prevents hyperlipidemia-induced fatty liver mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress by activating the AMPK-pgc-1α/Nrf2 pathway.Redox Biol. 2024 Aug;74:103230. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103230. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38875959 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of herbal drugs to treat heart failure: The roles of Sirt1/AMPK.J Pharm Anal. 2024 Feb;14(2):157-176. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.09.001. Epub 2023 Sep 27. J Pharm Anal. 2024. PMID: 38464786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Appraisal of Glycerylmonostearate/chitosan Hybrid Nanocapsules As Peroral Delivery System of Simvastatin.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 May 20;26(5):143. doi: 10.1208/s12249-025-03135-2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 40389763
-
Mechanisms of Myocardial Damage Due to Hyperlipidemia: A Review of Recent Studies.Med Sci Monit. 2022 Sep 16;28:e937051. doi: 10.12659/MSM.937051. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 36110037 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bozkurt B., Aguilar D., Deswal A., Dunbar S.B., Francis G.S., Horwich T., Jessup M., Kosiborod M., Pritchett A.M., Ramasubbu K., et al. Contributory Risk and Management of Comorbidities of Hypertension, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Hyperlipidemia, and Metabolic Syndrome in Chronic Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;134:e535–e578. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000450. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

