Mechanisms of Resistance to Anti-CD38 Daratumumab in Multiple Myeloma
- PMID: 31936617
- PMCID: PMC7017193
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9010167
Mechanisms of Resistance to Anti-CD38 Daratumumab in Multiple Myeloma
Abstract
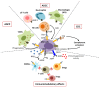
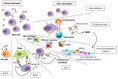
Daratumumab (Dara) is the first-in-class human-specific anti-CD38 mAb approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma (MM). Although recent data have demonstrated very promising results in clinical practice and trials, some patients do not achieve a partial response, and ultimately all patients undergo progression. Dara exerts anti-MM activity via antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and immunomodulatory effects. Deregulation of these pleiotropic mechanisms may cause development of Dara resistance. Knowledge of this resistance may improve the therapeutic management of MM patients.
Keywords: CD38 antigen; daratumumab; drug resistance; multiple myeloma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Solimando A.G., Da Vià M.C., Cicco S., Leone P., Di Lernia G., Giannico D., Desantis V., Frassanito M.A., Morizio A., Delgado Tascon J., et al. High-Risk Multiple Myeloma: Integrated Clinical and Omics Approach Dissects the Neoplastic Clone and the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Clin. Med. 2019;8:997. doi: 10.3390/jcm8070997. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Usmani S., Ahmadi T., Ng Y., Lam A., Desai A., Potluri R., Mehra M. Analysis of Real-World Data on Overall Survival in Multiple Myeloma Patients With ≥3 Prior Lines of Therapy Including a Proteasome Inhibitor (PI) and an Immunomodulatory Drug (IMiD), or Double Refractory to a PI and an IMiD. Oncologist. 2016;21:1355–1361. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

