Exploring the Multi-Target Performance of Mitochondriotropic Antioxidants against the Pivotal Alzheimer's Disease Pathophysiological Hallmarks
- PMID: 31936622
- PMCID: PMC7024345
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25020276
Exploring the Multi-Target Performance of Mitochondriotropic Antioxidants against the Pivotal Alzheimer's Disease Pathophysiological Hallmarks
Abstract
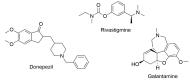
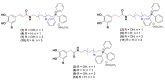
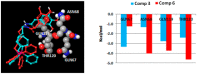
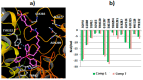
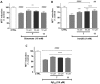
Alzheimer disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease featuring progressive and degenerative neurological impairments resulting in memory loss and cognitive decline. The specific mechanisms underlying AD are still poorly understood, but it is suggested that a deficiency in the brain neurotransmitter acetylcholine, the deposition of insoluble aggregates of fibrillar β-amyloid 1-42 (Aβ42), and iron and glutamate accumulation play an important role in the disease progress. Despite the existence of approved cholinergic drugs, none of them demonstrated effectiveness in modifying disease progression. Accordingly, the development of new chemical entities acting on more than one target is attracting progressively more attention as they can tackle intricate network targets and modulate their effects. Within this endeavor, a series of mitochondriotropic antioxidants inspired on hydroxycinnamic (HCA's) scaffold were synthesized, screened toward cholinesterases and evaluated as neuroprotectors in a differentiated human SH-SY5Y cell line. From the series, compounds 7 and 11 with a 10-carbon chain can be viewed as multi-target leads for the treatment of AD, as they act as dual and bifunctional cholinesterase inhibitors and prevent the neuronal damage caused by diverse aggressors related to protein misfolding and aggregation, iron accumulation and excitotoxicity.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; cholinesterase inhibitors; excitotoxicity; iron accumulation; mitochondriotropic antioxidants; oxidative stress; β-amyloid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Traub M., Freedman S.B. The Implication of Current Therapeutic Approaches for the Cholinergic Hypothesis of Dementia. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. 1992;3:189–192. doi: 10.1159/000107015. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

