Role of microRNAs as Clinical Cancer Biomarkers for Ovarian Cancer: A Short Overview
- PMID: 31936634
- PMCID: PMC7016727
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9010169
Role of microRNAs as Clinical Cancer Biomarkers for Ovarian Cancer: A Short Overview
Abstract
Ovarian cancer has the highest mortality rate among gynecological cancers. Early clinical signs are missing and there is an urgent need to establish early diagnosis biomarkers. MicroRNAs are promising biomarkers in this respect. In this paper, we review the most recent advances regarding the alterations of microRNAs in ovarian cancer. We have briefly described the contribution of miRNAs in the mechanisms of ovarian cancer invasion, metastasis, and chemotherapy sensitivity. We have also summarized the alterations underwent by microRNAs in solid ovarian tumors, in animal models for ovarian cancer, and in various ovarian cancer cell lines as compared to previous reviews that were only focused the circulating microRNAs as biomarkers. In this context, we consider that the biomarker screening should not be limited to circulating microRNAs per se, but rather to the simultaneous detection of the same microRNA alteration in solid tumors, in order to understand the differences between the detection of nucleic acids in early vs. late stages of cancer. Moreover, in vitro and in vivo models should also validate these microRNAs, which could be very helpful as preclinical testing platforms for pharmacological and/or molecular genetic approaches targeting microRNAs. The enormous quantity of data produced by preclinical and clinical studies regarding the role of microRNAs that act synergistically in tumorigenesis mechanisms that are associated with ovarian cancer subtypes, should be gathered, integrated, and compared by adequate methods, including molecular clustering. In this respect, molecular clustering analysis should contribute to the discovery of best biomarkers-based microRNAs assays that will enable rapid, efficient, and cost-effective detection of ovarian cancer in early stages. In conclusion, identifying the appropriate microRNAs as clinical biomarkers in ovarian cancer might improve the life quality of patients.
Keywords: biomarker; early diagnosis; microRNA; molecular clustering analysis; ovarian cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
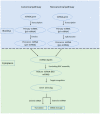
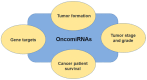
References
-
- NCI Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Cancer Stat Facts: Ovarian Cancer. [(accessed on 14 October 2019)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/ovary.html.
-
- Ehdaivand S. WHO Classification of Ovarian Neoplasms. [(accessed on 14 October 2019)]; Available online: https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorwhoclassif.html.
-
- NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms: Biomarker. [(accessed on 14 October 2019)]; Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/biomarker.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

