Alginate-Based Aerogel Particles as Drug Delivery Systems: Investigation of the Supercritical Adsorption and In Vitro Evaluations
- PMID: 31936834
- PMCID: PMC7014114
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13020329
Alginate-Based Aerogel Particles as Drug Delivery Systems: Investigation of the Supercritical Adsorption and In Vitro Evaluations
Abstract
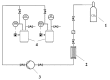
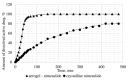
The present work focuses on the preparation of alginate-based aerogels in the form of particles for their further study as potential drug delivery systems (solid dosage forms). The dripping method was used to prepare certain gel particles, and supercritical drying was used to obtain final alginate-based aerogel particles. Three model active substances (ketoprofen, nimesulide, loratadine) were impregnated into the obtained aerogels using the supercritical adsorption process. Using the method of X-ray analysis, it was shown that the in the obtained drug-loaded aerogels the corresponding active substances are in an amorphous state, and the stability of this state after six months of storage is confirmed. In vitro dissolution tests for obtained drug-loaded aerogels was performed. For each sample, an appropriate dissolution medium (with certain pH) was determined. In vitro investigations showed the increasing of the release rate for all model active substances. Time was required to release and dissolve 50% of the active drug from drug-loaded aerogels (T1/2), reduced in comparison with pure active drugs in crystalline form. Obtained results provide insight into the application of alginate-based aerogel particles as a drug delivery system to improve pharmacokinetic properties of certain active drugs.
Keywords: X-ray analysis; adsorption; aerogel; amorphization; drug delivery systems; in vitro tests; supercritical fluids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures











References
-
- Aegerter M.A., Leventis N., Koebel M.M. Aerogels Handbook. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2011. Advances in Sol-Gel Derived Materials and Technologies.
-
- Lu T., Li Q., Chen W., Yu H. Composite aerogels based on dialdehyde nanocellulose and collagen for potential applications as wound dressing and tissue engineering scaffold. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014;94:132–138. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2014.01.020. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

