Divergent Evolution of Eukaryotic CC- and A-Adding Enzymes
- PMID: 31936900
- PMCID: PMC7014341
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21020462
Divergent Evolution of Eukaryotic CC- and A-Adding Enzymes
Abstract
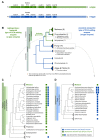
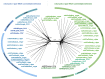
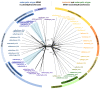
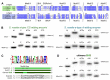
Synthesis of the CCA end of essential tRNAs is performed either by CCA-adding enzymes or as a collaboration between enzymes restricted to CC- and A-incorporation. While the occurrence of such tRNA nucleotidyltransferases with partial activities seemed to be restricted to Bacteria, the first example of such split CCA-adding activities was reported in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Here, we demonstrate that the choanoflagellate Salpingoeca rosetta also carries CC- and A-adding enzymes. However, these enzymes have distinct evolutionary origins. Furthermore, the restricted activity of the eukaryotic CC-adding enzymes has evolved in a different way compared to their bacterial counterparts. Yet, the molecular basis is very similar, as highly conserved positions within a catalytically important flexible loop region are missing in the CC-adding enzymes. For both the CC-adding enzymes from S. rosetta as well as S. pombe, introduction of the loop elements from closely related enzymes with full activity was able to restore CCA-addition, corroborating the significance of this loop in the evolution of bacterial as well as eukaryotic tRNA nucleotidyltransferases. Our data demonstrate that partial CC- and A-adding activities in Bacteria and Eukaryotes are based on the same mechanistic principles but, surprisingly, originate from different evolutionary events.
Keywords: Salpingoeca rosetta; Schizosaccharomyces pombe; enzyme evolution; tRNA nucleotidyltransferase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CCA-Addition Gone Wild: Unusual Occurrence and Phylogeny of Four Different tRNA Nucleotidyltransferases in Acanthamoeba castellanii.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Mar 9;38(3):1006-1017. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa270. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33095240 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of tRNA nucleotidyltransferases: a small deletion generated CC-adding enzymes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jun 10;105(23):7953-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801971105. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18523015 Free PMC article.
-
Schizosaccharomyces pombe contains separate CC- and A-adding tRNA nucleotidyltransferases.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Jan 15;508(3):785-790. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.131. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 30528393
-
tRNA-nucleotidyltransferases: highly unusual RNA polymerases with vital functions.FEBS Lett. 2010 Jan 21;584(2):297-302. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.078. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 19883645 Review.
-
tRNA nucleotidyltransferases: ancient catalysts with an unusual mechanism of polymerization.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 May;67(9):1447-63. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0271-4. Epub 2010 Feb 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20155482 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unusual Occurrence of Two Bona-Fide CCA-Adding Enzymes in Dictyostelium discoideum.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 23;21(15):5210. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155210. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32717856 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation of the Romanomermis culicivorax CCA-Adding Enzyme to Miniaturized Armless tRNA Substrates.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 28;21(23):9047. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239047. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33260740 Free PMC article.
-
CCA-addition in the cold: Structural characterization of the psychrophilic CCA-adding enzyme from the permafrost bacterium Planococcus halocryophilus.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Oct 21;19:5845-5855. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.10.018. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34765099 Free PMC article.
-
CCA-Addition Gone Wild: Unusual Occurrence and Phylogeny of Four Different tRNA Nucleotidyltransferases in Acanthamoeba castellanii.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Mar 9;38(3):1006-1017. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa270. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33095240 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deutscher M.P. 7 tRNA Nucleotidyltransferase. In: Boyer P.D., editor. The Enzymes: Volume XV: Nucleic Acids, Part B. 3rd ed. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 1982. pp. 183–215.
-
- Sprinzl M., Cramer F. The -C-C-A End of tRNA and Its Role in Protein Biosynthesis. In: Cohn W.E., editor. Progress in Nucleic Acid Research and Molecular Biology. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: London, UK: 1979. pp. 1–69. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

