Correlation of Wnt antagonist sFPR1, Slug and β-catenin with prognosis and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma
- PMID: 31938110
- PMCID: PMC6957938
Correlation of Wnt antagonist sFPR1, Slug and β-catenin with prognosis and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma
Abstract
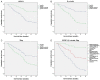
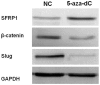
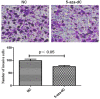
sFPR1 plays an important role in colorectal carcinoma (CRC) tumorigenesis, Slug is also considered to be related to the development of CRC. However, the relationship between them and the mechanism of their involvement in CRC metastasis remain unknown. In this study, immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to detect the expression of sFPR1, β-catenin, and Slug in 145 samples of CRC and corresponding surrounding "normal" mucosa tissues. Furthermore, clinicopathological features such as age, sex and so on were also collected retrospectively. Western blot and Transwell were used to detect proteins expression and migration capacity. In present study, the expression of sFPR1, Slug and β-catenin proteins were significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis and tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage of patients with CRC. sFPR1 expression showed a negative correlation with Slug and β-catenin. Kaplan-Meier analysis indicated that the postoperative 5-year OS of patients was related to the expression of sFPR1 and Slug, multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that sFPR1 expression was an independent prognostic factor for CRC patients. Moreover, we found that the expression of slug and β-catenin could be regulated by sFPR1 in SW480 cells, and migration capacity of SW480 cells was suppressed with sFPR1 restoration. In summary, our data suggest that sFRP1, Slug and β-catenin are related to metastasis and prognosis in CRC. sFPR1 could mediate CRC metastasis by regulating the expression of Slug and β-catenin. Combined detection of these factors may be of significant value in predicting the metastasis and prognosis in CRC patients.
Keywords: CRC; metastasis; prognosis; sFPR1; slug; β-catenin.
IJCEP Copyright © 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The correlation of KAI1, Slug and vasculogenic mimicry in the prediction of metastasis and prognosis in colorectal carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Oct 1;11(10):5034-5043. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31949580 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the correlation of KAI1/CD82, CD44, MMP7 and β-catenin in the prediction of prognosis and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma.Diagn Pathol. 2015 Sep 25;10:176. doi: 10.1186/s13000-015-0411-0. Diagn Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26408312 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of Slug and Vimentin as novel predictive biomarkers for lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Nov;34(11):2548-57. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt282. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 24001454
-
[T Cell Factor 4, beta-catenin and SFRP1 Expression of Wnt Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Carcinoma and the Prognosis].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Aug;32(4):854-61. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26710459 Chinese.
-
Interaction of the Wnt/β-catenin and RAS-ERK pathways involving co-stabilization of both β-catenin and RAS plays important roles in the colorectal tumorigenesis.Adv Biol Regul. 2018 May;68:46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Adv Biol Regul. 2018. PMID: 29449169 Review.
Cited by
-
The correlation of KAI1, Slug and vasculogenic mimicry in the prediction of metastasis and prognosis in colorectal carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Oct 1;11(10):5034-5043. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31949580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China. 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, DeSantis C, Virgo K, Stein K, Mariotto A, Smith T, Cooper D, Gansler T, Lerro C, Fedewa S, Lin C, Leach C, Cannady RS, Cho H, Scoppa S, Hachey M, Kirch R, Jemal A, Ward E. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:220–41. - PubMed
-
- Mina LA, Sledge GW Jr. Rethinking the metastatic cascade as a therapeutic target. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8:325–32. - PubMed
-
- Fodde R, Smits R, Clevers H. APC, signal transduction and genetic instability in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1:55–67. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Ji Q, Fan Z, Li Q. Cellular signaling pathways implicated in metastasis of colorectal cancer and the associated targeted agents. Future Oncol. 2015;11:2911–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
