Effect of soluble factors derived from ZR 75.30 breast cancer cells on endothelial activation
- PMID: 31938154
- PMCID: PMC6957993
Effect of soluble factors derived from ZR 75.30 breast cancer cells on endothelial activation
Abstract
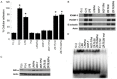
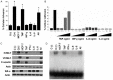
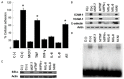
In this study, we analyzed soluble factors secreted by two Estrogen Receptor Positive (ER-α) human breast cancer cell lines, ZR 75.30 (luminal B) and MCF7 (luminal A), and evaluated their effect on endothelial activation. The composition of tumoral soluble factors (TSFs) was analyzed by ELISA (Bio-Plex). TSFs from ZR 75.30 cells expressed higher levels of TNF, IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-8 compared to TSFs from MCF-7 cells. TSFs from ZR 75.30 cells induced a pro-adhesive phenotype in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), as characterized by increased monocytic cell adhesion, adhesion molecule expression and NF-κB activation and decreased IκB-α expression. Conversely, TSFs from MCF-7 cells exerted none of these effects on HUVECs. We then added TNF, IFN-γ, IL-6 or IL-8 alone or in combination with TSFs from MCF-7 cells to HUVECs. Only the combinations that included TNF induced endothelial activation. A neutralizing antibody against IL-1β (this cytokine was not measured in the ELISA) had a modest blocking effect on cellular adhesion or the expression of adhesion molecules induced by TSFs from ZR 75.30 cells in HUVECs. However neutralizing antibodies against TNF, IFN-γ, IL-6 or IL-8 had no effect. Our results suggest that although TNF is an inducer of endothelial cell activation, it is not the only molecule that is responsible for this effect in TSFs from ZR 75.30 cells.
Keywords: TNF; Tumoral soluble factors; breast cancer; endothelial activation; endothelial cell adhesion molecules.
IJCEP Copyright © 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massagué J. Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:274–284. - PubMed
-
- Lu X, Kang Y. Organotropism of breast cancer metastasis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12:153–162. - PubMed
-
- Reymond N, D’Água BB, Ridley AJ. Crossing the endothelial barrier during metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:858–870. - PubMed
-
- Nariţa D, Seclaman E, Ursoniu S, Ilina R, Cireap N, Anghel A. Expression of CCL18 and interleukin-6 in the plasma of breast cancer patients as compared with benign tumor patients and healthy controls. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2011;52:1261–1267. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
