Improving Cognition via Exercise (ICE): Study Protocol for a Multi-Site, Parallel-Group, Single-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial Examining the Efficacy of Aerobic Exercise to Improve Neurocognition, Daily Functioning, and Biomarkers of Cognitive Change in Individuals with Schizophrenia
- PMID: 31938726
- PMCID: PMC6958554
- DOI: 10.20900/jpbs.20190020
Improving Cognition via Exercise (ICE): Study Protocol for a Multi-Site, Parallel-Group, Single-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial Examining the Efficacy of Aerobic Exercise to Improve Neurocognition, Daily Functioning, and Biomarkers of Cognitive Change in Individuals with Schizophrenia
Abstract
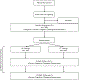
Individuals with schizophrenia (SZ) display cognitive deficits that have been identified as major determinants of poor functioning and disability, representing a serious public health concern and an important target for interventions. At present, available treatments offer only minimal to moderate benefits to ameliorate cognitive deficits. Thus, there remains an urgent need to identify novel interventions to improve cognition in people with SZ. Emerging evidence from animal and basic human research suggests aerobic exercise training (AE) has beneficial effects on cognition. Preliminary findings suggest that AE is efficacious in improving cognitive functioning in SZ, however the extant studies have been limited by small samples, a dearth of information on biologically-relevant covariates, and limited information on impact on daily functioning. Additionally, while AE-related cognitive benefits have been linked to Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) upregulation, this putative mechanism needs confirmation. The present report describes a study protocol designed to address these limitations-we review and summarize the current literature on treatment of cognitive deficits in SZ, state the rationale for employing AE to target these deficits, and describe the current protocol-a multi-site, single-blind, randomized clinical trial aiming to recruit 200 community-dwelling individuals with SZ. Participants are randomized to one of two 12-week interventions: AE using active-play video games (i.e., Xbox Kinect) and traditional cardiovascular exercise equipment or a stretching-and-toning (ST) control intervention. Participants undergo assessments of aerobic fitness, cognition, and daily functioning, as well as BDNF and other biomarkers of cognitive change, at baseline and after 6-and 12-weeks.
Keywords: BDNF; aerobic exercise; aerobic fitness; cognition; functioning; inflammation; neuroplasticity; neurotrophins; schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declares that they have no conflicts of interest associated with this project.
Figures
References
-
- Green MF, Kern RS, Heaton RK. Longitudinal studies of cognition and functional outcome in schizophrenia: Implications for MATRICS. Schizophr Res. 2004;72(1):41–51. - PubMed
-
- Green MF, Nuechterlein KH, Gold JM, Barch DM, Cohen J, Essock S, et al. Approaching a consensus cognitive battery for clinical trials in schizophrenia: The NIMH-MATRICS conference to select cognitive domains and test criteria. Biol Psychiatry. 2004. September 1;56(5):301–7. - PubMed
-
- Nuechterlein KH, Barch DM, Gold JM, Goldberg TE, Green MF, Heaton RK. Identification of separable cognitive factors in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2004;72(1):29–39. - PubMed
-
- Gold JM. Cognitive deficits as treatment targets in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2004;72(1):21–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical