Therapeutic Advances for Huntington's Disease
- PMID: 31940909
- PMCID: PMC7016861
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci10010043
Therapeutic Advances for Huntington's Disease
Abstract
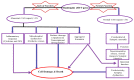
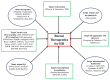
Huntington's disease (HD) is a progressive neurological disease that is inherited in an autosomal fashion. The cause of disease pathology is an expansion of cytosine-adenine-guanine (CAG) repeats within the huntingtin gene (HTT) on chromosome 4 (4p16.3), which codes the huntingtin protein (mHTT). The common symptoms of HD include motor and cognitive impairment of psychiatric functions. Patients exhibit a representative phenotype of involuntary movement (chorea) of limbs, impaired cognition, and severe psychiatric disturbances (mood swings, depression, and personality changes). A variety of symptomatic treatments (which target glutamate and dopamine pathways, caspases, inhibition of aggregation, mitochondrial dysfunction, transcriptional dysregulation, and fetal neural transplants, etc.) are available and some are in the pipeline. Advancement in novel therapeutic approaches include targeting the mutant huntingtin (mHTT) protein and the HTT gene. New gene editing techniques will reduce the CAG repeats. More appropriate and readily tractable treatment goals, coupled with advances in analytical tools will help to assess the clinical outcomes of HD treatments. This will not only improve the quality of life and life span of HD patients, but it will also provide a beneficial role in other inherited and neurological disorders. In this review, we aim to discuss current therapeutic research approaches and their possible uses for HD.
Keywords: CAG repeat; Huntington’s disease; mutant huntingtin (mHTT); neurodegeneration; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Antioxidants in Huntington's Disease: an Extensive Review.Neurotox Res. 2019 Apr;35(3):739-774. doi: 10.1007/s12640-018-9989-9. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 30632085 Review.
-
Towards a comprehensive understanding of the contributions of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of Huntington's disease.J Neurosci Res. 2019 Nov;97(11):1455-1468. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24492. Epub 2019 Jul 15. J Neurosci Res. 2019. PMID: 31304621 Review.
-
Latest advances on new promising molecular-based therapeutic approaches for Huntington's disease.J Transl Int Med. 2024 May 21;12(2):134-147. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2023-0142. eCollection 2024 Apr. J Transl Int Med. 2024. PMID: 38779119 Free PMC article.
-
Huntington's disease mouse models: unraveling the pathology caused by CAG repeat expansion.Fac Rev. 2021 Oct 21;10:77. doi: 10.12703/r/10-77. eCollection 2021. Fac Rev. 2021. PMID: 34746930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple clinical features of Huntington's disease correlate with mutant HTT gene CAG repeat lengths and neurodegeneration.J Neurol. 2019 Mar;266(3):551-564. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-8940-6. Epub 2018 Jun 28. J Neurol. 2019. PMID: 29956026 Review.
Cited by
-
Coenzyme Q10 effects in neurological diseases.Physiol Res. 2021 Dec 30;70(Suppl4):S683-S714. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934712. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 35199552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNM3OS regulates GAPDH expression and influences the molecular pathogenesis of Huntington's disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Sep;25(18):9066-9071. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16838. Epub 2021 Aug 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34369082 Free PMC article.
-
New Avenues for the Treatment of Huntington's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 4;22(16):8363. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168363. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copper, Iron, and Manganese Toxicity in Neuropsychiatric Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 22;22(15):7820. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157820. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HGF/c-Met Axis: The Advanced Development in Digestive System Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 26;8:801. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00801. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moss D.J.H., Pardinas A.F., Langbehn D., Lo K., Leavitt B.R., Roos R., Durr A., Mead S., TRACK-HD investigators. REGISTRY investigators et al. Identification of genetic variants associated with Huntington’s disease progression: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16:701–711. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30161-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

