Ureaplasma urealyticum disseminated multifocal abscesses in an immunocompromised adult patient: a case report
- PMID: 31941460
- PMCID: PMC6964043
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-4771-z
Ureaplasma urealyticum disseminated multifocal abscesses in an immunocompromised adult patient: a case report
Abstract
Background: Ureaplasma urealyticum is a fastidious bacteria which lacks a cell wall. Extragenital infections are rare in immunocompetent adults. There are few literature reports of perinephric abscess. We present a case of non-resolving multifocal "culture-negative" abscesses in a hypogammaglobulinemic adult female due to U. urealyticum.
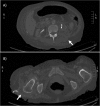
Case presentation: 66-year-old female with a one-week history of fever, malaise and new right hip and leg pain. Past medical history was notable for chronic pancytopenia secondary to in remission B cell follicular lymphoma, ESRD on intermittent hemodialysis with bilateral nephrostomy tubes and Crohn's. CT abdomen/pelvis revealed a small left perinephric hematoma and proximal right femur fluid collection. Persistent right thigh pain led to additional ultrasound with anterior thigh collection and CT revealed an irregular rim-enhancing fluid collection in the left posterior pararenal space. Antimicrobial therapy included ertapenem and vancomycin followed by meropenem, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, daptomycin and metronidazole in setting of persistent culture-negative results and clinical deterioration. Following detection of U. urealyticum by 16S rDNA PCR in both left pararenal and right trochanteric bursa abscesses doxycycline was started. Despite this, the patient died four days later.
Conclusions: Disseminated infection by U. urealyticum has been documented in immunocompromised adult patients with few reports of perinephric abscess. We propose that ascending genitourinary route led to perinephric abscess. The multiple disseminated fluid collections make it highly suspicious for hematogenous spread given the lack of radiographic enhancement to suggest contiguous spread. Diagnosis and treatment of U. urealyticum-disseminated infection is extremely challenging as culture is laborious and not routinely performed. Furthermore, the lack of cell wall renders beta-lactams and vancomycin ineffective and therefore requirement for "atypical" coverage. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to prevent further complications and death.
Keywords: Adult patient; Case report; Multifocal abscesses; Ureaplasma urealyticum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Septic arthritis of the shoulder due to Ureaplasma urealyticum after emergency caesarean section: a case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Oct 17;20(1):767. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05497-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33069221 Free PMC article.
-
Disseminated septic arthritis caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum in an immunocompromised patient with hypogammaglobulinemia after rituximab therapy.Infection. 2024 Dec;52(6):2495-2499. doi: 10.1007/s15010-024-02301-1. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Infection. 2024. PMID: 38856807 Free PMC article.
-
Ureaplasma parvum ventriculitis related to surgery and ventricular peritoneal drainage.J Infect Chemother. 2020 May;26(5):513-515. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2019.12.017. Epub 2020 Jan 29. J Infect Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32007385
-
Ureaplasma: current perspectives.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2015 Apr-Jun;33(2):205-14. doi: 10.4103/0255-0857.154850. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25865969 Review.
-
Role of erythromycin for treatment of incipient chronic lung disease in preterm infants colonised with Ureaplasma urealyticum.Drugs. 2001;61(13):1893-9. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200161130-00002. Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11708762 Review.
Cited by
-
Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) for the detection and quantification of Ureaplasma spp.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Aug 11;21(1):804. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06355-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34380416 Free PMC article.
-
A Unique Case Linking Rituximab to a Ureaplasma Infection and Life-Threatening Hyperammonemia.Cureus. 2024 Nov 25;16(11):e74426. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74426. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39723307 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical implications of the genus Mycoplasma].Rev Esp Quimioter. 2021 Jun;34(3):169-184. doi: 10.37201/req/014.2021. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2021. PMID: 33735544 Free PMC article. Review. Spanish.
-
Recurrent Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum in an Immunocompromised Adult Patient: A Case Report.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Nov 28;15:6863-6868. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S390096. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36465813 Free PMC article.
-
Refractory Bilateral Tubo-Ovarian Abscesses in a Patient with Iatrogenic Hypogammaglobulinemia.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 19;13(22):3478. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13223478. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leli C, Mencacci A, Agnese M, et al. ScienceDirect Prevalence of cervical colonization by Ureaplasma parvum , Ureaplasma urealyticum , Mycoplasma hominis and Mycoplasma genitalium in childbearing age women by a commercially available multiplex real-time PCR : An Italian observational multicentre study. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2018;51(2):220–225. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2017.05.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Regan Joan A, Greenberg EM. Perinatal Ureaplasma urealyticum infection and colonization: the association with preterm delivery and the spectrum of disease in neonates. Rev Med Microbiol. 2001;12(2):97–107. doi: 10.1097/00013542-200104000-00004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous