Desmosomes: Essential contributors to an integrated intercellular junction network
- PMID: 31942240
- PMCID: PMC6944264
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.20942.1
Desmosomes: Essential contributors to an integrated intercellular junction network
Abstract
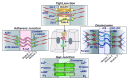
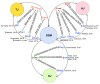
The development of adhesive connections between cells was critical for the evolution of multicellularity and for organizing cells into complex organs with discrete compartments. Four types of intercellular junction are present in vertebrates: desmosomes, adherens junctions, tight junctions, and gap junctions. All are essential for the development of the embryonic layers and organs as well as adult tissue homeostasis. While each junction type is defined as a distinct entity, it is now clear that they cooperate physically and functionally to create a robust and functionally diverse system. During evolution, desmosomes first appeared in vertebrates as highly specialized regions at the plasma membrane that couple the intermediate filament cytoskeleton at points of strong cell-cell adhesion. Here, we review how desmosomes conferred new mechanical and signaling properties to vertebrate cells and tissues through their interactions with the existing junctional and cytoskeletal network.
Keywords: Adherens junctions; Cadherins; Connexins; Cytoskeleton; Gap Junctions; Intermediate Filaments; Tight junctions.
Copyright: © 2019 Green KJ et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

