Human C-peptide Quantitation by LC-MS Isotope-Dilution Assay in Serum or Urine Samples
- PMID: 31942247
- PMCID: PMC6961834
- DOI: 10.4172/2157-7064.1000172
Human C-peptide Quantitation by LC-MS Isotope-Dilution Assay in Serum or Urine Samples
Abstract
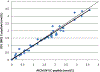
In this communication we report a simple and efficient approach to C-peptide quantitation using isotope dilution mass-spectrometry analysis. The method facilitates quantitation of C-peptide levels at least one order of magnitude lower compared to concentration levels achieved with an IDA method reported previously. The improvement was due to more intensive sample preparation procedure that, in turn, makes it possible to increase the sample load without a corresponding increase in matrix effects. We also show the results of a comparison study with a second laboratory using a similar previously reported method for C-peptide quantitation.
Keywords: C-peptide/Mass spectrometry; Ion Exchange chromatography; Isotope dilution assay; Sample preparation.
Figures

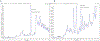
References
-
- Sun W, Gao X, Zhao X, Cui D, Xia Q (2010) Beneficial effects of C-peptide on renal morphology in diabetic rats. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 42: 893–899. - PubMed
-
- Steiner DF, Cunningham D, Spigelman L, Aten B (1967) Insulin biosynthesis: evidence for a precursor. Science 157: 697–700. - PubMed
-
- Eaton RP, Allen RC, Schade DS (1983) Hepatic removal of insulin normal man: dose response to endogenous insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 56: 1294–1300. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
