Nasal Skin Thickness Measurements Using Computed Tomography in an Adult Saudi Population
- PMID: 31942407
- PMCID: PMC6908396
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000002450
Nasal Skin Thickness Measurements Using Computed Tomography in an Adult Saudi Population
Abstract
Rhinoplasty is one of the most challenging operations in plastic surgery, and nasal skin thickness is a significant factor in determining rhinoplasty success. Only a few studies have measured nasal skin thickness before rhinoplasty. The present study was designed to measure nasal skin thickness to shed light on its importance to successful rhinoplasty.
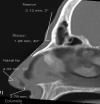
Methods: Altogether, 60 patients underwent measurements of nasal skin thickness at 4 aesthetic points: nasion, rhinion, nasal tip, columella. The thickness was measured using computed tomography (CT), an objective, reliable tool for this purpose. Universally adopted Hounsfield unit measurement using in house software (Consultant Radiology Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia) was performed using CT scan.
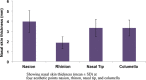
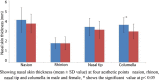
Results: The study group included 32 women and 28 men. Age range was 18-68 years, but most of the patients (53.3%) were within the 20-30-year age range. CT results showed that the mean nasal skin thickness was 3.96 ± 1.08 mm at the nasion, 1.86 ± 0.62 mm at the rhinion, 3.32 ± 0.78 mm at the nasal tip, and 3.32 ± 0.73 mm at the columella. When the nasal skin thicknesses were compared between men and women, a significant difference was observed only at the columella (P = 0.016).
Conclusions: The nasal skin is thickest at the nasion, thinner at the rhinion, and again thicker at the nasal tip and columella. Our data could be useful for plastic surgeons who could take the patient's own nasal area thickness into consideration when planning his or her rhinoplasty.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures
References
-
- Keyes GR. Commentary on: incidence and preoperative risk factors for major complications in aesthetic rhinoplasty: analysis of 4978 patients. Aesthet Surg J. 2017;37:768. - PubMed
-
- Hafezi F, Naghibzadeh B, Nouhi A. Management of the thick-skinned nose: a more effective approach. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2006;115:444–449. - PubMed
-
- Whitaker EG, Johnson CM., Jr. Skin and subcutaneous tissue in rhinoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2002;26(suppl 1):S19. - PubMed
-
- Lai A, Cheney ML. External nasal anatomy and its application to rhinoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2002;26(suppl 1):S9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
