Polysomnographic assessment of suvorexant in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease dementia and insomnia: a randomized trial
- PMID: 31944580
- PMCID: PMC7984350
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.12035
Polysomnographic assessment of suvorexant in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease dementia and insomnia: a randomized trial
Abstract
Introduction: We evaluated the clinical profile of the orexin receptor antagonist suvorexant for treating insomnia in patients with mild-to-moderate probable Alzheimer's disease (AD) dementia.
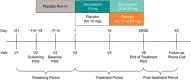
Methods: Randomized, double-blind, 4-week trial of suvorexant 10 mg (could be increased to 20 mg based on clinical response) or placebo in patients who met clinical diagnostic criteria for both probable AD dementia and insomnia. Sleep was assessed by overnight polysomnography in a sleep laboratory. The primary endpoint was change-from-baseline in polysomnography-derived total sleep time (TST) at week 4.
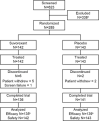
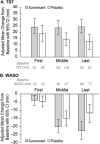
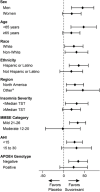
Results: Of 285 participants randomized (suvorexant, N = 142; placebo, N = 143), 277 (97%) completed the trial (suvorexant, N = 136; placebo, N = 141). At week 4, the model-based least squares mean improvement-from-baseline in TST was 73 minutes for suvorexant and 45 minutes for placebo; (difference = 28 minutes [95% confidence interval 11-45], p < 0.01). Somnolence was reported in 4.2% of suvorexant-treated patients and 1.4% of placebo-treated patients.
Discussion: Suvorexant improved TST in patients with probable AD dementia and insomnia.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02750306.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; insomnia; randomized clinical trial; suvorexant.
© 2020 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
W.J.H., P.C., E.S., K.B., J.H., J.S., C.L., and D.M. are current or former employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. (MSD), a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA, and they own or owned stock options in Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA. D.B. has acted as a consultant for Merck & Co., Inc. (Kenilworth, NJ USA), Jazz, Eisai, and Ferring.
Figures
References
-
- Zhao QF, Tan L, Wang HF, et al. The prevalence of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer's disease: systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Affect Disord. 2016;190:264‐271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

