Alternating patterns of seasonal influenza activity in the WHO European Region following the 2009 pandemic, 2010-2018
- PMID: 31944604
- PMCID: PMC7040975
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.12703
Alternating patterns of seasonal influenza activity in the WHO European Region following the 2009 pandemic, 2010-2018
Abstract
Background: Influenza virus infections are common and lead to substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide. We characterized the first eight influenza epidemics since the 2009 influenza pandemic by describing the distribution of viruses and epidemics temporally and geographically across the WHO European Region.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed laboratory-confirmed influenza detections in ambulatory patients from sentinel sites. Data were aggregated by reporting entity and season (weeks 40-20) for 2010-2011 to 2017-2018. We explored geographical spread using correlation coefficients.
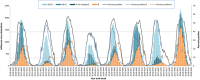
Results: There was variation in the regional influenza epidemics during the study period. Influenza A virus subtypes alternated in dominance, except for 2013-2014 during which both cocirculated, and only one season (2017-2018) was B virus dominant. The median start week for epidemics in the Region was week 50, the time to the peak ranged between four and 13 weeks, and the duration of the epidemic ranged between 19 and 25 weeks. There was evidence of a west-to-east spread across the Region during epidemics in 2010-2011 (r = .365; P = .019), 2012-2013 (r = .484; P = .001), 2014-2015 (r = .423; P = .006), and 2017-2018 (r = .566; P < .001) seasons. Variation in virus distribution and timing existed within reporting entities across seasons and across reporting entities for a given season.
Conclusions: Aggregated influenza detection data from sentinel surveillance sites by season between 2010 and 2018 have been presented for the European Region for the first time. Substantial diversity exists between influenza epidemics. These data can inform prevention and control efforts at national, sub-national, and international levels. Aggregated, regional surveillance data from early affected reporting entities may provide an early warning function and be helpful for early season forecasting efforts.
Keywords: Central Asia; Europe; influenza; surveillance.
© 2019 The Authors. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- WHO . WHO recommendations on the composition of influenza virus vaccines. Available at http://www.who.int/influenza/vaccines/virus/recommendations/en/. Accessed 24 December 2018.
-
- GHO . By category. Population ‐ Data by WHO region. Available at http://apps.who.int/gho/data/view.main.POP2020. Accessed 24 December 2018.
-
- Flu News Europe; Home. Available at https://flunewseurope.org/. Accessed 8 December 2016.
-
- Influenza surveillance country profiles of WHO European Region Member States. Available at http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/communicable-diseases/influenza.... Accessed 18 January 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

