Targeting the Host for New Therapeutic Perspectives in Hepatitis D
- PMID: 31947588
- PMCID: PMC7019876
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9010222
Targeting the Host for New Therapeutic Perspectives in Hepatitis D
Abstract
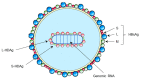
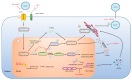
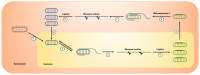
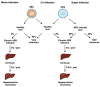
Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a small satellite virus of hepatitis B virus (HBV) requiring HBV infection to complete its life cycle. It has been recently estimated that 13% of chronic HBV infected patients (60 million) are co-infected with HDV. Chronic hepatitis D is the most severe form of viral hepatitis with the highest risk to develop cirrhosis and liver cancer. Current treatment is based on pegylated-interferon-alpha which rarely controls HDV infection and is complicated by serious side effects. The development of novel antiviral strategies based on host targeting agents has shown promising results in phase I/II clinical trials. This review summarizes HDV molecular virology and physiopathology as well as new therapeutic approaches targeting HDV host factors.
Keywords: Hepatitis D; antiviral strategy; host factors; liver disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rizzetto M., Canese M.G., Aricò S., Crivelli O., Trepo C., Bonino F., Verme G. Immunofluorescence detection of new antigen-antibody system (delta/anti-delta) associated to hepatitis B virus in liver and in serum of HBsAg carriers. Gut. 1977;18:997–1003. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.12.997. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fattovich G., Giustina G., Schalm S.W., Hadziyannis S., Sanchez-Tapias J., Almasio P., Christensen E., Krogsgaard K., Degos F., de Moura M.C., et al. Occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensation in western European patients with cirrhosis type B. The EUROHEP Study Group on Hepatitis B Virus and Cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1995;21:77–82. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

