Anti-PD-1 and Novel Combinations in the Treatment of Melanoma-An Update
- PMID: 31947592
- PMCID: PMC7019511
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9010223
Anti-PD-1 and Novel Combinations in the Treatment of Melanoma-An Update
Abstract
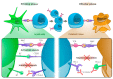
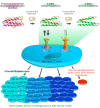
Until recently, distant metastatic melanoma was considered refractory to systemic therapy. A better understanding of the interactions between tumors and the immune system and the mechanisms of regulation of T-cells led to the development of immune checkpoint inhibitors. This review summarizes the current novel data on the treatment of metastatic melanoma with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antibodies and anti-PD-1-based combination regimens, including clinical trials presented at major conference meetings. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, in particular anti-PD-1 antibodies such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab and the combination of nivolumab with the anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) antibody ipilimumab can achieve long-term survival for patients with metastatic melanoma. The anti-PD-1 antibodies nivolumab and pembrolizumab were also approved for adjuvant treatment of patients with resected metastatic melanoma. Anti-PD-1 antibodies appear to be well tolerated, and toxicity is manageable. Nivolumab combined with ipilimumab achieves a 5 year survival rate of more than 50% but at a cost of high toxicity. Ongoing clinical trials investigate novel immunotherapy combinations and strategies (e.g., Talimogene laherparepvec (T-VEC), Bempegaldesleukin (BEMPEG), incorporation or sequencing of targeted therapy, incorporation or sequencing of radiotherapy), and focus on poor prognosis groups (e.g., high tumor burden/LDH levels, anti-PD-1 refractory melanoma, and brain metastases).
Keywords: BEMPEG; IDO1; LAG-3; PD-1; PD-L1; T-VEC; acral melanoma; adjuvant therapy; brain metastases; combination therapies; desmoplastic melanoma; melanoma; mucosal melanoma; neoadjuvant therapy; novel combinations; uveal mealnoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hodi F.S., Kluger H., Sznol M., Carvajal R., Lawrence D., Atkins M., Powderly J., Sharfman W., Puzanov I., Smith D., et al. Abstract CT001: Durable, long-term survival in previously treated patients with advanced melanoma (MEL) who received nivolumab (NIVO) monotherapy in a phase I trial. Cancer Res. 2016;76:CT001.
-
- Robert C., Ribas A., Wolchok J.D., Hodi F.S., Hamid O., Kefford R., Weber J.S., Joshua A.M., Hwu W.J., Gangadhar T.C., et al. Anti-programmed-death-receptor-1 treatment with pembrolizumab in ipilimumab-refractory advanced melanoma: A randomised dose-comparison cohort of a phase 1 trial. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2014;384:1109–1117. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60958-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hamid O., Robert C., Daud A., Hodi F.S., Hwu W.J., Kefford R., Wolchok J.D., Hersey P., Joseph R., Weber J.S., et al. Five-year survival outcomes for patients with advanced melanoma treated with pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-001. Ann. Oncol. 2019;30:582–588. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

