Potential impacts of a novel integrated extracorporeal-CPR workflow using an interventional radiology and immediate whole-body computed tomography system in the emergency department
- PMID: 31948395
- PMCID: PMC6964082
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-020-01332-4
Potential impacts of a novel integrated extracorporeal-CPR workflow using an interventional radiology and immediate whole-body computed tomography system in the emergency department
Abstract
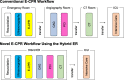
Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) can be associated with increased survival and neurologic benefits in selected patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). However, there remains insufficient evidence to recommend the routine use of ECPR for patients with OHCA. A novel integrated trauma workflow concept that utilizes a sliding computed tomography (CT) scanner and interventional radiology (IR) system, named a hybrid emergency room system (HERS), allowing emergency therapeutic interventions and CT examination without relocating trauma patients, has recently evolved in Japan. HERS can drastically shorten the ECPR implementation time and more quickly facilitate definitive interventions than the conventional advanced cardiovascular life support workflow. Herein, we discuss our novel workflow concept using HERS on ECPR for patients with OHCA.
Keywords: Concurrent treatment; Emergency department; Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation; HERS; Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kinoshita Takahiro, Yamakawa Kazuma, Matsuda Hiroki, Yoshikawa Yoshiaki, Wada Daiki, Hamasaki Toshimitsu, Ono Kota, Nakamori Yasushi, Fujimi Satoshi. The Survival Benefit of a Novel Trauma Workflow that Includes Immediate Whole-body Computed Tomography, Surgery, and Interventional Radiology, All in One Trauma Resuscitation Room. Annals of Surgery. 2019;269(2):370–376. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002527. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

