The impact of chronic widespread pain on health status and long-term health predictors: a general population cohort study
- PMID: 31948483
- PMCID: PMC6966859
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-020-3039-5
The impact of chronic widespread pain on health status and long-term health predictors: a general population cohort study
Abstract
Background: Chronic widespread pain (CWP) has a negative impact on health status, but results have varied regarding gender-related differences and reported health status. The aim was to study the impact of CWP on health status in women and men aged 35-54 years in a sample of the general population. The aim was further to investigate lifestyle-related predictors of better health status in those with CWP in a 12- and 21-year perspective.
Method: A general population cohort study including 975 participants aged 35-54 years, with a 12- and 21-year follow-up. CWP was measured with a pain mannequin, and the questionnaire included questions on lifestyles factors with SF-36 for measurement of health status. Differences in health status were analysed with independent samples t-test and health predictors with logistic regression analysis.
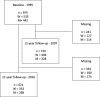
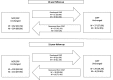
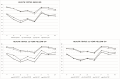
Results: The prevalence of CWP was higher in women at all time points, but health status was reduced in both women and men with CWP (p < 0.001) with no gender differences of clinical relevance. At the 12-year follow-up, a higher proportion of women than men had developed CWP (OR 2.04; CI 1.27-3.26), and at the 21-year follow-up, a higher proportion of men had recovered from CWP (OR 3.79; CI 1.00-14.33). In those reporting CWP at baseline, a better SF-36 health status (Physical Functioning, Vitality or Mental Health) at the 12-year follow-up was predicted by male gender, having personal support, being a former smoker, and having no sleeping problems. In the 21-year follow-up, predictors of better health were male gender, a weekly intake of alcohol, and having no sleeping problems.
Conclusion: Women and men with CWP have the same worsening of health status, but men recover from CWP to a greater extent in the long-term. Being male, having social support, being a former smoker, and having no sleeping problems were associated with better health status in those with CWP.
Keywords: Chronic widespread pain; Gender differences; Health predictors; Health status.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Treede R-D, Rief W, Barke A, Aziz Q, Bennett MI, Benoliel R, et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: the IASP classification of chronic pain for the international classification of diseases:(: ICD-11:). Pain. 2019;160:19–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

