A network analysis to identify mediators of germline-driven differences in breast cancer prognosis
- PMID: 31949161
- PMCID: PMC6965101
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-14100-6
A network analysis to identify mediators of germline-driven differences in breast cancer prognosis
Abstract
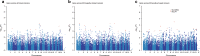
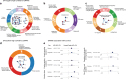
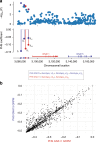
Identifying the underlying genetic drivers of the heritability of breast cancer prognosis remains elusive. We adapt a network-based approach to handle underpowered complex datasets to provide new insights into the potential function of germline variants in breast cancer prognosis. This network-based analysis studies ~7.3 million variants in 84,457 breast cancer patients in relation to breast cancer survival and confirms the results on 12,381 independent patients. Aggregating the prognostic effects of genetic variants across multiple genes, we identify four gene modules associated with survival in estrogen receptor (ER)-negative and one in ER-positive disease. The modules show biological enrichment for cancer-related processes such as G-alpha signaling, circadian clock, angiogenesis, and Rho-GTPases in apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
A.Ashworth is a cofounder of Tango Therapeutics, Azkarra Therapeutics, and Ovibio, is an advisor for Gladiator, Prolynx, Bluestar, Earli and Genentech, reports receiving commercial research grants from AstraZeneca and SPARC, and has ownership interest in patents on the use of PARP inhibitors, held jointly with AstraZeneca. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA176785/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA176726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA092044/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA058223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148112/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098758/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 16942/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- 19187/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MR/M012190/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA164917/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA199277/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA179715/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA128931/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA156733/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_14105/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097396/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 29186/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA176726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA058860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA177150/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16563/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA077398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA132839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA058860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA192393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

