MiR-106a-5p promotes 5-FU resistance and the metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting TGFβR2
- PMID: 31949649
- PMCID: PMC6963073
MiR-106a-5p promotes 5-FU resistance and the metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting TGFβR2
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)-based chemotherapy has always been the first-line treatment. However, development of 5-FU resistance seriously affects its curative effect. The aim of this study was to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of 5-FU resistance through miR-106a-5p in CRC.
Methods: Colorectal cancer tissues were collected to analyze miR-106a-5p and TGFβR2 expressions by qPCR. Functional experiments for evaluating cell survival and metastasis were conducted to observe the biological effects of miR-106a-5p and TGFβR2. The cell survival rate was calculated using an MTT assay; the metastasis was confirmed with a Transwell invasion assay and Western blotting, which we used to measure the expression levels of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers E-cadherin and vimentin. The combination of miR-106a to TGFβR2 was predicted using Targetscan, and confirmed through the construction of the luciferase reporter plasmid pGL3-basic. The interplay between miR-106a-5p and TGFβR2 was tested with qPCR and Western blotting. A Spearman rank analysis was employed to verify the correlation of miR-106a-5p and TGFβR2 expressions.
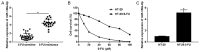
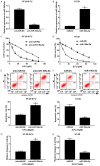
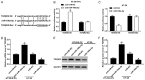
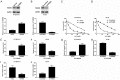
Results: MiR-106a-5p was up-regulated and TGFβR2 was down-regulated in 5-FU resistant CRC tissues and HT-29 cells. MiR-106a-5p promoted cell survival and suppressed the apoptosis rate and caspase 3 activity. Additionally, cell invasion was promoted by miR-106a-5p overexpression in the HT-29 cells and was inhibited by miR-106a-5p knockdown in the 5-FU resistant HT-29 cells; miR-106a-5p overexpression contributed to migration by increasing vimentin expression and by decreasing E-cadherin expression in the HT-29 cells; miR-106a-5p functioned by directly binding to TGFβR2. The TGFβR2 knockdown conferred chemoresistance of 5-FU and metastasis in 5-FU resistant HT-29 cells, and TGFβR2 overexpression reduced cell survival, invasion numbers, vimentin expression, and increased the cell apoptosis rate and caspase 3 activity in 5-FU resistant HT-29 cells. Also, miR-106a-5p negatively regulated TGFβR2 in a linear correlation way in the CRC tissues.
Conclusion: The up-regulation of miR-106a-5p contributes to the pathomechanism of colorectal cancer by promoting 5-FU resistance and metastasis via inhibiting target TGFβR2. Our findings provide new promising ways for the clinical application of the TGFβR2-miR-106a axis in clinical chemotherapy for 5-FU resistant colorectal cancer.
Keywords: 5-FU resistance; MiR-106a-5p; TGFβR2; colorectal cancer; metastasis.
IJCEP Copyright © 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GDPD5, a target of miR-195-5p, is associated with metastasis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:945-952. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.028. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29635904
-
The long non-coding RNA HOTAIRM1 suppresses cell progression via sponging endogenous miR-17-5p/ B-cell translocation gene 3 (BTG3) axis in 5-fluorouracil resistant colorectal cancer cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep;117:109171. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109171. Epub 2019 Jun 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31261026
-
LncRNA-HCG18 regulates the viability, apoptosis, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of papillary thyroid cancer cells via regulating the miR-106a-5p/PPP2R2A axis.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 May;221:153395. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153395. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 33798913
-
Overview of miR-106a Regulatory Roles: from Cancer to Aging.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jul 27;10(8):892. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10080892. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular determinants of response to 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in colorectal cancer: The undisputable role of micro-ribonucleic acids.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2020 Sep 15;12(9):942-956. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i9.942. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33005290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Updates on Mechanisms of Resistance to 5-Fluorouracil and Reversal Strategies in Colon Cancer Treatment.Biology (Basel). 2021 Aug 31;10(9):854. doi: 10.3390/biology10090854. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34571731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA VCAN-AS1 promotes the malignant behaviors of breast cancer by regulating the miR-106a-5p-mediated STAT3/HIF-1α pathway.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):5028-5044. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1960774. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34365889 Free PMC article.
-
KLF6-mediated recruitment of the p300 complex enhances H3K23su and cooperatively upregulates SEMA3C with FOSL2 to drive 5-FU resistance in colon cancer cells.Exp Mol Med. 2025 Mar;57(3):667-685. doi: 10.1038/s12276-025-01424-1. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Exp Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40082673 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic combinations of exosomes alongside cancer stem cells (CSCs) and of CSC-derived exosomes (CSCEXs) in cancer therapy.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Oct 5;24(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03514-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39369258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes Derived from Hypoxic Glioma Cells Reduce the Sensitivity of Glioma Cells to Temozolomide Through Carrying miR-106a-5p.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Oct 13;16:3589-3598. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S382690. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 36248244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li J, Li X, Cen C, Ai X, Lin C, Hu G. The long non-coding RNA ENST00000547547 reduces 5-fluorouracil resistance of colorectal cancer cells via competitive binding to microRNA-31. Oncol Rep. 2018;39:217–226. - PubMed
-
- Li PL, Zhang X, Wang LL, Du LT, Yang YM, Li J, Wang CX. MicroRNA-218 is a prognostic indicator in colorectal cancer and enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis by targeting BIRC5. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36:1484–1493. - PubMed
-
- Paydas S, Acikalin A, Ergin M, Celik H, Yavuz B, Tanriverdi K. Micro-RNA (miRNA) profile in Hodgkin lymphoma: association between clinical and pathological variables. Med Oncol. 2016;33:34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
