Chemical Composition and the Cytotoxic, Antimicrobial, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Fruit Peel Essential Oil from Spondias pinnata (Anacardiaceae) in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China
- PMID: 31952118
- PMCID: PMC7024216
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25020343
Chemical Composition and the Cytotoxic, Antimicrobial, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Fruit Peel Essential Oil from Spondias pinnata (Anacardiaceae) in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China
Abstract
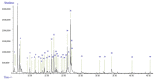
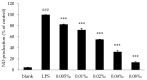
Spondias pinnata (Linn. f.) Kurz (Anacardiaceae) is widely distributed in tropical Asia, where it is commonly used as a vegetable and fruit, and is attracting increasing research attention. In this study, we investigated the chemical composition and the cytotoxic, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory activities of the fruit peel essential oil of S. pinnata (EOSP), which has been consumed as a medicine and condiment in Xishuangbanna, southwest China. A total of 40 components were identified by Gas Chromatography/Mass spectrometry (GC-MS), representing 95.19% of the EOSP, with furfural (17.14%), α-terpineol (13.09%), and ethyl benzoate (9.05%) as the main constituents. EOSP has moderate cytotoxic activity against five cancer cells and obvious antimicrobial activity against five pathogenic strains. In particular, EOSP (Minimal Inhibitory and Fungicidal Concentration, MIC and MFC, 16‒32 µg/mL) showed a 32-times higher inhibition effect against Aspergillus fumigatus than the positive control Tigecycline (MIC and MBC 512‒1024 µg/mL). EOSP also showed strong anti-inflammatory activity by significantly inhibiting nitric oxide (NO) production induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in RAW 264.7 cell lines at 0.08‱, with no effect on cell viability. These bioactivities of S. pinnata fruit peel validate its traditional uses and suggest that it could be a new source of natural antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agents for food or medical industries.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; Spondias pinnata; Xishuangbanna; anti-inflammatory; antimicrobial; essential oil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chemical composition, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities of the essential oil from Maqian (Zanthoxylum myriacanthum var. pubescens) in Xishuangbanna, SW China.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Dec 2;158 Pt A:43-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Oct 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25448503
-
Chemical composition, antioxidant, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities of the stem and leaf essential oils from Piper flaviflorum from Xishuangbanna, SW China.Nat Prod Commun. 2014 Jul;9(7):1011-4. Nat Prod Commun. 2014. PMID: 25230516
-
Chemical composition and biological activity of the essential oil obtained from Bupleurum marginatum (Apiaceae).J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;61(8):1079-87. doi: 10.1211/jpp/61.08.0012. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19703352
-
Odoriferous Therapy: A Review Identifying Essential Oils against Pathogens of the Respiratory Tract.Chem Biodivers. 2020 Jun;17(6):e2000062. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202000062. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Chem Biodivers. 2020. PMID: 32207224 Review.
-
Essential Oils from Neotropical Piper Species and Their Biological Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 14;18(12):2571. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122571. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29240662 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Shift of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in Gluten-Free Hemp-Enriched Sourdough Bread: A Metabolomic Approach.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 10;12(4):1050. doi: 10.3390/nu12041050. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32290149 Free PMC article.
-
Spondias sp: Shedding Light on Its Vast Pharmaceutical Potential.Molecules. 2023 Feb 16;28(4):1862. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041862. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential Oils in Respiratory Mycosis: A Review.Molecules. 2022 Jun 28;27(13):4140. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134140. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Composition and Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiviral, and Larvicidal Activities of the Essential Oils of Zanthoxylum acanthopodium DC. from China and Myanmar.Molecules. 2022 Aug 17;27(16):5243. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165243. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014481 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory potential of dichloromethane leaf extracts of Eucalyptus globulus (Labill) and Senna didymobotrya (Fresenius) in mice.Afr Health Sci. 2021 Mar;21(1):397-409. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v21i1.50. Afr Health Sci. 2021. PMID: 34394322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Combrinck S., Regnier T., Kamatou G.P.P. In Vitro activity of eighteen essential oils and some major components against common postharvest fungal pathogens of fruit. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2011;33:344–349. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2010.11.011. - DOI
-
- Shaaban H.A.E., El-Ghorab A.H., Shibamoto T. Bioactivity of essential oils and their volatile aroma components: Review. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2012;24:203–212. doi: 10.1080/10412905.2012.659528. - DOI
-
- Drummond R.A. Aspergillus fumigatus. [(accessed on 25 September 2019)]; Available online: https://www.immunology.org/public-information/bitesized-immunology/patho....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

