Hepatitis C Virus Affects Tuberculosis-Specific T Cells in HIV-Negative Patients
- PMID: 31952232
- PMCID: PMC7019953
- DOI: 10.3390/v12010101
Hepatitis C Virus Affects Tuberculosis-Specific T Cells in HIV-Negative Patients
Abstract
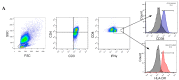
The occurrence of tuberculosis (TB) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections in the same patient presents a unique clinical challenge. The impact of HCV infection on the immune response to TB remains poorly investigated in TB+/HCV+ patients. This study was conducted to evaluate the impact of HCV on the T-cell-mediated immune response to TB in coinfected patients. Sixty-four patients with active TB infections were screened for coinfection with HCV. The expression of immune activation markers IFN-γ, CD38, and HLA-DR on TB-specific CD4+ T cells was evaluated by flow cytometry in TB-monoinfected patients, TB/HCV-coinfected patients, and healthy controls. IL-2, IL-4, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-10 levels were measured using ELISA. The end-of-treatment response to anti-TB therapy was recorded for both patient groups. Significantly lower levels of CD4+IFN-γ+CD38+ and CD4+IFN-γ+HLA-DR+ T cells were detected in TB/HCV-coinfected patients compared to TB monoinfected patients and controls. TB+/HCV+-coinfected patients showed higher serum levels of IL-10. The baseline frequencies of TB-specific activated T-cell subsets did not predict the response to antituberculous therapy in TB+/HCV+ patients. We concluded that different subsets of TB-specific CD4+ T cells in TB/HCV-infected individuals are partially impaired in early-stage HCV infection. This was combined with increased serum IL-10 level. Such immune modulations may represent a powerful risk factor for disease progression in patients with HCV/TB coinfection.
Keywords: IL-10; T cells; TB/HCV coinfection; hepatitis C virus; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . Global Tuberculosis Report 2019. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2019. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
-
- Lomtadze N., Kupreishvili L., Salakaia A., Vashakidze S., Sharvadze L., Kempker R.R., Magee M.J., del Rio C., Blumberg H.M. Hepatitis c virus co-infection increases the risk of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity among patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e83892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083892. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

