Low-dose-aspirin usage among women with an increased preeclampsia risk: A prospective cohort study
- PMID: 31953956
- PMCID: PMC7317843
- DOI: 10.1111/aogs.13808
Low-dose-aspirin usage among women with an increased preeclampsia risk: A prospective cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Low-dose aspirin (LDA) prophylaxis has been shown to reduce women's preeclampsia risk. Evidence regarding LDA adherence rates of pregnant women is based almost exclusively on clinical trials, giving a potentially biased picture. Moreover, these studies do not report on determinants of adherence. Since 2017, obstetric healthcare professionals in a Dutch region have assessed women's preeclampsia risk by means of a prediction tool and counseled those with an above-population average risk on LDA as a prophylactic measure.
Material and methods: From 2017 to 2018, 865 women were recruited in multiple centers and prospectively followed using web-based surveys (Expect Study II). Rates and determinants of LDA usage among women with an increased preeclampsia risk in daily practice were assessed. Results were compared with findings in a similar cohort from a care-as-usual setting lacking risk-based counseling (Expect Study I, n = 2614). Netherlands Trial Register NTR4143.
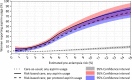
Results: In total, 306 women had a predicted increased preeclampsia risk. LDA usage was higher for women receiving risk-based care than care-as-usual (29.4% vs 1.5%, odds ratio 19.1, 95% confidence interval 11.2-32.5). Daily LDA usage was positively correlated with both predicted risk and women's concerns regarding preeclampsia. Most reported reasons for non- or incomplete use were unawareness of LDA as a preventive intervention, concerns about potential adverse effects and doubts regarding the benefits.
Conclusions: Risk-based counseling was associated with a higher prevalence of LDA usage, but general usage rates were low. Future research regarding potential factors improving the usage of LDA during pregnancy is necessary.
Keywords: adherence; aspirin; preeclampsia; pregnancy.
© 2020 The Authors. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology (NFOG).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Mol BWJ, Roberts CT, Thangaratinam S, Magee LA, de Groot CJM, Hofmeyr GJ. Pre‐eclampsia. Lancet. 2016;387:999‐1011. - PubMed
-
- Roberge S, Bujold E, Nicolaides KH. Aspirin for the prevention of preterm and term preeclampsia: systematic review and metaanalysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218:287‐293.e1. - PubMed
-
- Allen R, Rogozinska E, Sivarajasingam P, Khan KS, Thangaratinam S. Effect of diet‐ and lifestyle‐based metabolic risk‐modifying interventions on preeclampsia: a meta‐analysis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2014;93:973‐985. - PubMed
-
- Roberge S, Nicolaides K, Demers S, Hyett J, Chaillet N, Bujold E. The role of aspirin dose on the prevention of preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;216:110‐120.e6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

