CeRNA regulatory network-based analysis to study the roles of noncoding RNAs in the pathogenesis of intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 31956102
- PMCID: PMC7053603
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.102634
CeRNA regulatory network-based analysis to study the roles of noncoding RNAs in the pathogenesis of intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma
Abstract
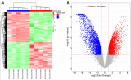
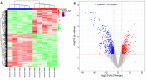
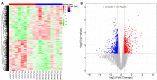
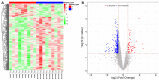
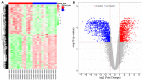
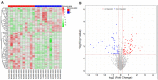
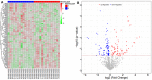
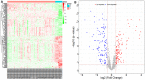
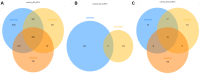
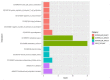
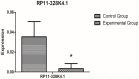
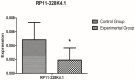
To explore and understand the competitive mechanism of ceRNAs in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC), we used bioinformatics analysis methods to construct an ICC-related ceRNA regulatory network (ceRNET), which contained 340 lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory relationships based on the RNA expression datasets in the NCBI GEO database. We identified the core regulatory pathway RP11-328K4.1-hsa-miR-27a-3p-PROS1, which is related to ICC, for further validation by molecular biology assays. GO analysis of 44 differentially expressed mRNAs in ceRNET revealed that they were mainly enriched in biological processes including "negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation" and "positive regulation of activated T lymphocyte proliferation." KEGG analysis showed that they were mainly enriched in the "complement and coagulation cascade" pathway. The molecular biology assay showed that lncRNA RP11-328K4.1 expression was significantly lower in the cancerous tissues and peripheral plasma of ICC patients than in normal controls (p<0.05). In addition, hsa-miR-27a-3p was found to be significantly upregulated in the cancer tissues and peripheral plasma of ICC patients (p<0.05). Compared to normal controls, the expression of PROS1 mRNA was significantly downregulated in ICC patient cancer tissues (p<0.05) but not in peripheral plasma (p>0.05). Furthermore, ROC analysis revealed that RP11-328K4.1, hsa-miR-27a-3p, and PROS1 had significant diagnostic value in ICC. We concluded that the upregulation of lncRNA RP11-328K4.1, which might act as a miRNA sponge, exerts an antitumor effect in ICC by eliminating the inhibition of PROS1 mRNA expression by oncogenic miRNA hsa-miR-27a.
Keywords: biomarkers; ceRNA; ceRNA regulatory network; intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Whole Transcriptome Sequencing Analyzes the Interactions of mRNAs and ncRNAs in Cholangiocarcinoma.Cancer Med. 2025 May;14(9):e70906. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70906. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40304434 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue.BMC Cancer. 2019 Aug 7;19(1):779. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5983-8. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31391008 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies the Estrogen Receptor 1 (ESR1) Gene and hsa-miR-26a-5p as Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in Patients with Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2020 May 21;26:e921815. doi: 10.12659/MSM.921815. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32435051 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Jan;21(1):177-184. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12951. Epub 2016 Sep 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 27619971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA RP3-525N10.2-NFKB1-PROS1 triplet-mediated low PROS1 expression is an onco-immunological biomarker in low-grade gliomas: a pan-cancer analysis with experimental verification.J Transl Med. 2022 Jul 25;20(1):335. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03536-y. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35879775 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miRNAs as a Tool for Early Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer-Implications for the Fertility-Sparing Process: Clinical, Biological, and Legal Aspects.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 12;24(14):11356. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411356. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of machine learning models for predicting prognosis and guiding individualized postoperative chemotherapy: A real-world study of distal cholangiocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 15;13:1106029. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1106029. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37007095 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of lncRNA LINC01234 Suppresses the Tumorigenesis of Liver Cancer via Sponging miR-513a-5p.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 16;10:571565. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.571565. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33178601 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of an HCC recurrence model basedon the investigation of immune-relatedlncRNAs and related mechanisms.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Nov 10;26:1387-1400. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.11.006. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34900397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Dicker D, Pain A, Hamavid H, Moradi-Lakeh M, MacIntyre MF, Allen C, Hansen G, Woodbrook R, Wolfe C, Hamadeh RR, Moore A, Werdecker A, et al., and Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. The Global Burden of Cancer 2013. JAMA Oncol. 2015; 1:505–27. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.0735 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

