Molecular pathobiology of scleritis and its therapeutic implications
- PMID: 31956585
- PMCID: PMC6942945
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2020.01.23
Molecular pathobiology of scleritis and its therapeutic implications
Abstract
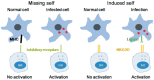
Scleritis and other autoimmune diseases are characterized by an imbalance in the levels of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory molecules with the balance tilted more towards the former due to the failure of recognition of self. The triggering of inflammatory process could be ascribed to the presence of cytoplasmic DNA/chromatin that leads to activation of cytosolic DNA-sensing cGAS-STING (cyclic GMP-AMP synthase linked to stimulator of interferon genes) pathway and enhanced expression of NF-κB that results in an increase in the production of pro-inflammatory bioactive lipids. Bioactive lipids gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), dihomo-GLA (DGLA), prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), prostacyclin (PGI2) and lipoxin A4, resolvins, protectins and maresins have anti-inflammatory actions, bind to DNA to render it non-antigenic and are decreased in autoimmune diseases. These results suggest that efforts designed to enhance the production of anti-inflammatory bioactive lipids may form a new approach to autoimmune diseases. Local injection or infusion of lipoxins, resolvins, protectins and maresins or their precursors such as arachidonic acid may be exploited in the prevention and management of autoimmune diseases including scleritis, uveitis and lupus/rheumatoid arthritis.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; bioactive lipids; cytokines; inflammation; micronucleus; resolution of inflammation; scleritis.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures



References
-
- Sainz de la Maza M, Foster CS, Jabbur NS. Scleritis-associated uveitis. Ophthalmology. 1997;104(1):58–63. - PubMed
-
- Cohn M. The common sense of the self-nonself discrimination. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2005;27(1):3–17. - PubMed
-
- Diefenbach A, Raulet DH. Strategies for target cell recognition by natural killer cells. Immunol Rev. 2001;181:170–184. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
