Simultaneous Left Ventricular Volume and Strain Changes During Chemotherapy Associate With 2-Year Postchemotherapy Measures of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 31959033
- PMCID: PMC7033821
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.119.015400
Simultaneous Left Ventricular Volume and Strain Changes During Chemotherapy Associate With 2-Year Postchemotherapy Measures of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction
Abstract
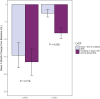
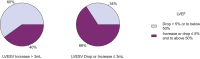
Background Although changes in left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV), left ventricular end-diastolic volume, and global circumferential strain occur during cancer treatment, the relationship of these changes to the 2-year post-cancer-treatment measures of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) are unknown. Methods and Results In a prospective, continuously recruited cohort of 95 patients scheduled to receive potentially cardiotoxic chemotherapy for breast cancer, lymphoma, or soft tissue sarcoma, measures of left ventricular end-diastolic volume, LVESV, global circumferential strain, and LVEF were acquired via cardiac magnetic resonance imaging before and then 3 and 24 months after initiating treatment by individuals blinded to all patient identifiers. Participants had an average age of 54±15 years; 68% were women, and 82% were of white race. LVEF declined from 62±7% to 58±9% over the 24 months (P<0.0001), with 42% of participants experiencing a >5% decline in LVEF at 24 months. Predictors of a 24-month >5% decline in LVEF included the following factors from baseline to 3 months into treatment: (1) >3-mL increases in LVESV (P=0.033), (2) >3-mL increases in LVESV or 10-mL declines in left ventricular end-diastolic volume with little change in LVESV (P=0.001), or (3) ≥10% deteriorations in global circumferential strain with little change in LVESV (P=0.036). Conclusion During receipt of potentially cardiotoxic chemotherapy, increases in LVESV, the absence of its deterioration during decreases of left ventricular end-diastolic volume, or the deterioration of global circumferential strain without a marked decrease in LVESV help identify those who will develop more permanent 2-year declines in LVEF.
Keywords: cardiotoxicity; chemotherapy; global circumferential strain; left ventricular ejection fraction.
Figures

References
-
- Meléndez GC, Sukpraphrute B, D'Agostino RB, Jordan JH, Klepin HD, Ellis L, Lamar Z, Vasu S, Lesser G, Burke GL, Weaver KE, Ntim WO, Hundley WG. Frequency of left ventricular end‐diastolic volume–mediated declines in ejection fraction in patients receiving potentially cardiotoxic cancer treatment. Am J Cardiol. 2017;119:1637–1642. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heckbert SR, Post W, Pearson GD, Arnett DK, Gomes AS, Jerosch‐Herold M, Hundley WG, Lima JA, Bluemke DA. Traditional cardiovascular risk factors in relation to left ventricular mass, volume, and systolic function by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: the Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:2285–2292. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

