Prediction of octanol-water partition coefficients for the SAMPL6- molecules using molecular dynamics simulations with OPLS-AA, AMBER and CHARMM force fields
- PMID: 31960254
- PMCID: PMC7667952
- DOI: 10.1007/s10822-019-00267-z
Prediction of octanol-water partition coefficients for the SAMPL6- molecules using molecular dynamics simulations with OPLS-AA, AMBER and CHARMM force fields
Abstract
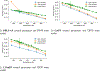
All-atom molecular dynamics simulations with stratified alchemical free energy calculations were used to predict the octanol-water partition coefficient of eleven small molecules as part of the SAMPL6- blind prediction challenge using four different force field parametrizations: standard OPLS-AA with transferable charges, OPLS-AA with non-transferable CM1A charges, AMBER/GAFF, and CHARMM/CGenFF. Octanol parameters for OPLS-AA, GAFF and CHARMM were validated by comparing the density as a function of temperature, the chemical potential, and the hydration free energy to experimental values. The partition coefficients were calculated from the solvation free energy for the compounds in water and pure ("dry") octanol or "wet" octanol with 27 mol% water dissolved. Absolute solvation free energies were computed by thermodynamic integration (TI) and the multistate Bennett acceptance ratio with uncorrelated samples from data generated by an established protocol using 5-ns windowed alchemical free energy perturbation (FEP) calculations with the Gromacs molecular dynamics package. Equilibration of sets of FEP simulations was quantified by a new measure of convergence based on the analysis of forward and time-reversed trajectories. The accuracy of the predictions was assessed by descriptive statistical measures such as the root mean square error (RMSE) of the data set compared to the experimental values. Discarding the first 1 ns of each 5-ns window as an equilibration phase had a large effect on the GAFF data, where it improved the RMSE by up to 0.8 log units, while the effect for other data sets was smaller or marginally worsened the agreement. Overall, CGenFF gave the best prediction with RMSE 1.2 log units, although for only eight molecules because the current CGenFF workflow for Gromacs does not generate files for certain halogen-containing compounds. Over all eleven compounds, GAFF gave an RMSE of 1.5. The effect of using a mixed water/octanol solvent slightly decreased the accuracy for CGenFF and GAFF and slightly increased it for OPLS-AA. The GAFF and OPLS-AA results displayed a systematic error where molecules were too hydrophobic whereas CGenFF appeared to be more balanced, at least on this small data set.
Keywords: AMBER force field; CHARMM force field; Free energy perturbation; Ligand parametrization; Molecular dynamics; OPLS-AA force field; Octanol-water partition coefficient; Solvation free energy.
Figures

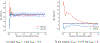
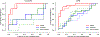


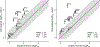


Similar articles
-
Precise force-field-based calculations of octanol-water partition coefficients for the SAMPL7 molecules.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021 Jul;35(7):853-870. doi: 10.1007/s10822-021-00407-4. Epub 2021 Jul 7. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021. PMID: 34232435 Free PMC article.
-
SAMPL6 blind predictions of water-octanol partition coefficients using nonequilibrium alchemical approaches.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2020 Apr;34(4):371-384. doi: 10.1007/s10822-019-00233-9. Epub 2019 Oct 17. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2020. PMID: 31624982
-
SAMPL6 Octanol-water partition coefficients from alchemical free energy calculations with MBIS atomic charges.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2020 Apr;34(4):327-334. doi: 10.1007/s10822-020-00281-6. Epub 2020 Jan 20. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2020. PMID: 31960251
-
Is AMOEBA a Good Force Field for Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Carbohydrates?J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Jun 9;65(11):5289-5300. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00442. Epub 2025 May 20. J Chem Inf Model. 2025. PMID: 40392062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolution of the Amber additive protein force field: History, current status, and future.J Chem Phys. 2025 Jan 21;162(3):030901. doi: 10.1063/5.0227517. J Chem Phys. 2025. PMID: 39817575 Review.
Cited by
-
SAMPL7 blind challenge: quantum-mechanical prediction of partition coefficients and acid dissociation constants for small drug-like molecules.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021 Jul;35(7):841-851. doi: 10.1007/s10822-021-00402-9. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021. PMID: 34164769
-
Evaluation of log P, pKa, and log D predictions from the SAMPL7 blind challenge.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021 Jul;35(7):771-802. doi: 10.1007/s10822-021-00397-3. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021. PMID: 34169394 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral evaluation of hydroxyethylamine analogs: Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (3CLpro), a virtual screening and simulation approach.Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 Oct 1;47:116393. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116393. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34509862 Free PMC article.
-
Precise force-field-based calculations of octanol-water partition coefficients for the SAMPL7 molecules.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021 Jul;35(7):853-870. doi: 10.1007/s10822-021-00407-4. Epub 2021 Jul 7. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2021. PMID: 34232435 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of CHARMM force field parameters for ryanodine receptor inhibitory drug dantrolene using FFTK and FFParam.J Mol Model. 2024 Jan 23;30(2):46. doi: 10.1007/s00894-024-05841-3. J Mol Model. 2024. PMID: 38261112
References
-
- Bannan CC, Burley KH, Chiu M, Shirts MR, Gilson MK, Mobley DL (2016) Blind prediction of cyclohexane–water distribution coefficients from the SAMPL5 challenge. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design 30(11):927–944, DOI 10.1007/s10822-016-9954-8, URL 10.1007/s10822-016-9954-8 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

