Neuroprotective Effects of Necrostatin-1 Against Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Damage: an Involvement of Cathepsin D Inhibition
- PMID: 31960265
- PMCID: PMC7062871
- DOI: 10.1007/s12640-020-00164-6
Neuroprotective Effects of Necrostatin-1 Against Oxidative Stress-Induced Cell Damage: an Involvement of Cathepsin D Inhibition
Abstract
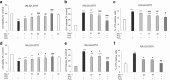
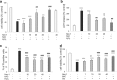
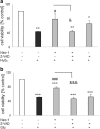
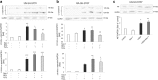
Necroptosis, a recently discovered form of non-apoptotic programmed cell death, can be implicated in many pathological conditions including neuronal cell death. Moreover, an inhibition of this process by necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) has been shown to be neuroprotective in in vitro and in vivo models of cerebral ischemia. However, the involvement of this type of cell death in oxidative stress-induced neuronal cell damage is less recognized. Therefore, we tested the effects of Nec-1, an inhibitor of necroptosis, in the model of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced cell damage in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y and murine hippocampal HT-22 cell lines. The data showed that Nec-1 (10-40 μM) attenuated the cell death induced by H2O2 in undifferentiated (UN-) and neuronal differentiated (RA-) SH-SY5Y cells with a higher efficacy in the former cell type. Moreover, Nec-1 partially reduced cell damage induced by 6-hydroxydopamine in UN- and RA-SH-SY5Y cells. The protective effect of Nec-1 was of similar magnitude as the effect of a caspase-3 inhibitor in both cell phenotypes and this effect were not potentiated after combined treatment. Furthermore, the non-specific apoptosis and necroptosis inhibitor curcumin augmented the beneficial effect of Nec-1 against H2O2-evoked cell damage albeit only in RA-SH-SY5Y cells. Next, it was found that the mechanisms of neuroprotective effect of Nec-1 against H2O2-induced cell damage in SH-SY5Y cells involved the inhibition of lysosomal protease, cathepsin D, but not caspase-3 or calpain activities. In HT-22 cells, Nec-1 was protective in two models of oxidative stress (H2O2 and glutamate) and that effect was blocked by a caspase inhibitor. Our data showed neuroprotective effects of the necroptosis inhibitor, Nec-1, against oxidative stress-induced cell damage and pointed to involvement of cathepsin D inhibition in the mechanism of its action. Moreover, a cell type-specific interplay between necroptosis and apoptosis has been demonstrated.
Keywords: Caspase-3; Glutamate; HT-22 cells; Hydrogen peroxide; Pepstatin A; SH-SY5Y cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The ATM kinase inhibitor KU-55933 provides neuroprotection against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell damage via a γH2AX/p-p53/caspase-3-independent mechanism: Inhibition of calpain and cathepsin D.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Jun;87:38-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.03.015. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28341201
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Methyl Caffeate against Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Cell Damage: Involvement of Caspase 3 and Cathepsin D Inhibition.Biomolecules. 2020 Nov 9;10(11):1530. doi: 10.3390/biom10111530. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33182454 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Arzanol against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress Damage in Differentiated and Undifferentiated SH-SY5Y Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 5;25(13):7386. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137386. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000492 Free PMC article.
-
Necrostatin-1 and necroptosis inhibition: Pathophysiology and therapeutic implications.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jan;163:105297. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105297. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33181319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Necroptotic Cell Death in Liver Transplantation and Underlying Diseases: Mechanisms and Clinical Perspective.Liver Transpl. 2019 Jul;25(7):1091-1104. doi: 10.1002/lt.25488. Liver Transpl. 2019. PMID: 31077562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tat-hspb1 Suppresses Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) Growth via Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;14(22):5710. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225710. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428802 Free PMC article.
-
An in vitro evaluation of the antioxidant activities of necroptosis and apoptosis inhibitors: the potential of necrostatin-1 and necrostatin-1i to have radical scavenging activities.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Apr;75(2):490-497. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00450-y. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36719636
-
Neuronal RBM5 modulates cell signaling responses to traumatic and hypoxic-ischemic injury in a sex-dependent manner.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Oct 17;9(1):379. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01677-7. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37848418 Free PMC article.
-
The role of lysosome in regulated necrosis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Oct;10(10):1880-1903. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 33163342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Evidence for the Interplay between Oxidative Stress and RIP1-Dependent Cell Death in Neurodegeneration: State of the Art and Possible Therapeutic Implications.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Sep 24;10(10):1518. doi: 10.3390/antiox10101518. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679652 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agholme L, Lindström T, Kågedal K, Marcusson J, Hallbeck M. An in vitro model for neuroscience: differentiation of SH-SY5Y cells into cells with morphological and biochemical characteristics of mature neurons. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20:1069–1082. - PubMed
-
- Askalan R, Gabarin N, Armstrong EA, Fang Liu Y, Couchman D, Yager JY. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration after severe hypoxic-ischemic injury in the neonatal rat brain. Brain Res. 2015;1629:94–103. - PubMed
-
- Biton S, Ashkenazi A. NEMO and RIP1 control cell fate in response to extensive DNA damage via TNF-α feedforward signaling. Cell. 2011;145:92–103. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

