Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in neurodegenerative diseases and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 31960806
- PMCID: PMC7047811
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.272576
Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in neurodegenerative diseases and therapeutic implications
Conflict of interest statement
None
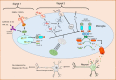
Figures
References
-
- Broz P, Dixit VM. Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16:407–420. - PubMed
-
- Dempsey C, Rubio Araiz A, Bryson KJ, Finucane O, Larkin C, Mills EL, Robertson AAB, Cooper MA, O’Neill LAJ, Lynch MA. Inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome with MCC950 promotes non-phlogistic clearance of amyloid-beta and cognitive function in APP/PS1 mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2017;61:306–316. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

