Systematic Identification of Host Immune Key Factors Influencing Viral Infection in PBL of ALV-J Infected SPF Chicken
- PMID: 31963363
- PMCID: PMC7019883
- DOI: 10.3390/v12010114
Systematic Identification of Host Immune Key Factors Influencing Viral Infection in PBL of ALV-J Infected SPF Chicken
Abstract
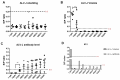
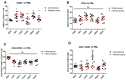
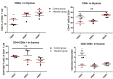
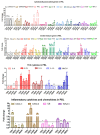
Although research related to avian leukosis virus subgroup J (ALV-J) has lasted for more than a century, the systematic identification of host immune key factors against ALV-J infection has not been reported. In this study, we establish an infection model in which four-week-old SPF chickens are infected with ALV-J strain CHN06, after which the host immune response is detected. We found that the expression of two antiviral interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) (Mx1 and IFIT5) were increased in ALV-J infected peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL). A significant CD8+ T cell response induced by ALV-J appeared as early as seven days post-infection (DPI), and humoral immunity starting from 21 DPI differed greatly in the time scale of induction level. Meanwhile, the ALV-J viremia was significantly decreased before antibody production at 14 DPI, and eliminated at 21 DPI under a very low antibody level. The up-regulated CD8+ T cell in the thymus (14DPI) and PBL (7 DPI and 21 DPI) was detected, indicating that the thymus may provide the output of CD8+ T cell to PBL, which was related to virus clearance. Besides, up-regulated chemokine CXCLi1 at 7 DPI in PBL was observed, which may be related to the migration of the CD8+ T cell from the thymus to PBL. More importantly, the CD8 high+ T cell response of the CD8αβ phenotype may produce granzyme K, NK lysin, or IFN-γ for clearing viruses. These findings provide novel insights and direction for developing effective ALV-J vaccines.
Keywords: ALV-J; CD8+ T cell response; PBL; chicken; phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Dai M.M., Feng M., Xie T.T., Li Y.F., Zhang X.Q. Fluctuations in luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, and progesterone might affect the disappearance of avian leukosis virus subgroup J viremia in chickens with intermittent viremia. Poult. Sci. 2019;98:3533–3538. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez195. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dou W.W., Li H.M., Cheng Z.Q., Zhao P., Liu J.X., Cui Z.Z., Liu H.G., Jing W.F., Guo H.J. Maternal antibody induced by recombinant gp85 protein vaccine adjuvanted with CpG-ODN protects against ALV-J early infection in chickens. Vaccine. 2013;31:6144–6149. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.06.058. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

