Gelatin Hydrolysate Hybrid Nanoparticles as Soft Edible Pickering Stabilizers for Oil-In-Water Emulsions
- PMID: 31963546
- PMCID: PMC7024373
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25020393
Gelatin Hydrolysate Hybrid Nanoparticles as Soft Edible Pickering Stabilizers for Oil-In-Water Emulsions
Abstract
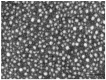
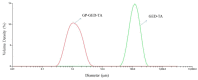
The aim of this study was to fabricate edible gelatin enzymic digest (GED) based gel particles that can stabilize oil-in-water (O/W) microemulsions. The gel particles were generated by covalent crosslinking, with genipin, the individual protein molecules within tannic acid-induced gelatin hydrolysate (GED-TA) particles. The ability of the genipin-treated GED-TA (GP-GED-TA) to stabilize emulsions was evaluated by Turbiscan analysis and droplet-size changes. For comparison, gelatin hydrolysate (GE) and tannic acid-induced gelatin hydrolysate particles (GED-TA) were used as controls. The mean diameters of GED, GED-TA, and GP-GED-TA particles were 0.68 ± 0.1 nm, 66.2 ± 8.4 nm, and 66.9 ± 7.2 nm, respectively. Nanomechanic analysis using atomic force microscopy(AFM) indicated the average Young's modulu of the GP-GED-TA particles was 760.8 ± 112.0 Mpa, indicating the GP-GED-TA were soft particles. The Turbiscan stability indexes (lower values indicate a more stable emulsion) of the emulsions stabilized with GED, GED-TA, and GP-GED-TA, after storage for three days, were 28.6 ± 1.5, 19.3 ± 4.8, and 4.4 ± 1.3, respectively. After one, or 60 days of storage, the volume-weighted mean diameters (D[4,3]) of oil droplets stabilized by GP-GED-TA were 1.19 ± 0.11 μm and 1.18 ± 0.1 µm, respectively. The D[4,3] of oil droplets stabilized by GED-TA, however, increased from 108.3 ± 5.1 μm to 164.3 ± 19.1 μm during the storage. Overall, the GP-GED-TA gel particles have considerable potential for stabilization of O/W emulsions in food products.
Keywords: edible pickering stabilizer; emulsifying property; gelatin hydrolysate hybrid; soft gel particles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Wei Z., Huang Q. Edible Pickering emulsions stabilized by ovotransferrin–gum arabic particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2019;89:590–601. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.11.037. - DOI
-
- Sanchez-Salvador J.L., Balea A., Monte M.C., Blanco A., Negro C. Pickering Emulsions Containing Cellulose Microfibers Produced by Mechanical Treatments as Stabilizer in the Food Industry. Appl. Sci. 2019;9:359. doi: 10.3390/app9020359. - DOI
-
- Liu X., Guo J., Wan Z.-L., Liu Y.-Y., Ruan Q.-J., Yang X.-Q. Wheat gluten-stabilized high internal phase emulsions as mayonnaise replacers. Food Hydrocoll. 2018;77:168–175. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.09.032. - DOI
-
- Murray B.S. Pickering emulsions for food and drinks. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019;27:57–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2019.05.004. - DOI
-
- Dai L., Sun C., Wei Y., Mao L., Gao Y. Characterization of Pickering emulsion gels stabilized by zein/gum arabic complex colloidal nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2018;74:239–248. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.07.040. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

