Naturally Occurring Isocoumarins Derivatives from Endophytic Fungi: Sources, Isolation, Structural Characterization, Biosynthesis, and Biological Activities
- PMID: 31963586
- PMCID: PMC7024277
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25020395
Naturally Occurring Isocoumarins Derivatives from Endophytic Fungi: Sources, Isolation, Structural Characterization, Biosynthesis, and Biological Activities
Abstract
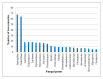
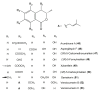
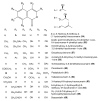
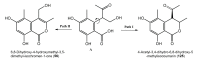
Recently, the metabolites separated from endophytes have attracted significant attention, as many of them have a unique structure and appealing pharmacological and biological potentials. Isocoumarins represent one of the most interesting classes of metabolites, which are coumarins isomers with a reversed lactone moiety. They are produced by plants, microbes, marine organisms, bacteria, insects, liverworts, and fungi and possessed a wide array of bioactivities. This review gives an overview of isocoumarins derivatives from endophytic fungi and their source, isolation, structural characterization, biosynthesis, and bioactivities, concentrating on the period from 2000 to 2019. Overall, 307 metabolites and more than 120 references are conferred. This is the first review on these multi-facetted metabolites from endophytic fungi.
Keywords: biological activities; biosynthesis; dihydroisocoumarins; endophytes; isocoumarins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




























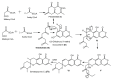
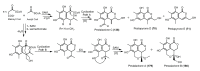

References
-
- Ibrahim S.R., Elkhayat E.S., Mohamed G.A., Khedr A.I., Fouad M.A., Kotb M.H., Ross S.A. Aspernolides F and G, new butyrolactones from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus. Phytochem. Lett. 2015;14:84–90. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2015.09.006. - DOI
-
- Ibrahim S.R., Mohamed G.A., Moharram A.M., Youssef D.T. Aegyptolidines A and B: New pyrrolidine alkaloids from the fungus Aspergillus aegyptiacus. Phytochem. Lett. 2015;12:90–93. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2015.03.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

