Evaluation of the Oxidative Stress Status in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Liver Induced by Three Typical Organic UV Filters (BP-4, PABA and PBSA)
- PMID: 31963911
- PMCID: PMC7027007
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17020651
Evaluation of the Oxidative Stress Status in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Liver Induced by Three Typical Organic UV Filters (BP-4, PABA and PBSA)
Abstract
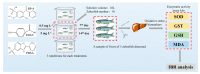
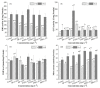
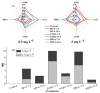
Organic UV filters are a kind of emerging pollutants, which have been widely used in personal care products (PCPs). This study evaluated the effects of benzophenone-4 (BP-4), 4-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), and 2-phenylbenzimidazole-5-sulfonic acid (PBSA) on the selected indices of antioxidative responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio) liver. Zebrafish were exposed to two different doses (i.e., 0.5 and 5 mg L-1) of semi-static water with three individual compounds. Liver samples were collected on 7 and 14 days to analyze biochemical indicators, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione S-transferase (GST), reduced glutathione (GSH), and malondialdehyde (MDA). Oxidative stress occurred in zebrafish liver with significantly changed indicators during the whole exposure period. Different experimental groups could induce or inhibit the activity of antioxidant enzymes with varying degrees. With a prolonged exposure time and increased exposure dose, the hepatic lipid peroxidation was also obviously observed. Moreover, the toxicity order of three organic UV filters was analyzed using the integrated biomarker response (IBR) index and the results indicate that exposure to PABA for 7 days at 0.5 mg L-1 and PBSA for 7 days at 5 mg L-1 induced the most severe oxidative stress in the liver of zebrafish.
Keywords: integrated biomarker response; lipid peroxidation; organic UV filters; oxidative stress; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Presence of UV filters in surface water and the effects of phenylbenzimidazole sulfonic acid on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) following a chronic toxicity test.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2013 Oct;96:41-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.06.022. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2013. PMID: 23906701
-
Antioxidative responses in zebrafish liver exposed to sublethal doses Aphanizomenon flos-aquae DC-1 aphantoxins.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2015 Mar;113:425-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.029. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2015. PMID: 25544652
-
Toxicity assessment of pyriproxyfen in vertebrate model zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio): A multi biomarker study.Aquat Toxicol. 2018 Mar;196:132-145. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.01.010. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Aquat Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29407799
-
Hepatic oxidative stress biomarker responses in freshwater fish Carassius auratus exposed to four benzophenone UV filters.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2015 Sep;119:116-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.05.017. Epub 2015 May 18. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2015. PMID: 25996523
-
Evaluation of toxicity of Personal Care Products (PCPs) in freshwaters: Zebrafish as a model.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2022 Aug;94:103923. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2022.103923. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35772612 Review.
Cited by
-
An Association between Insulin Resistance and Neurodegeneration in Zebrafish Larval Model (Danio rerio).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 27;23(15):8290. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158290. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955446 Free PMC article.
-
Advantages of omics technology for evaluating cadmium toxicity in zebrafish.Toxicol Res. 2021 Jan 25;37(4):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s43188-020-00082-x. eCollection 2021 Oct. Toxicol Res. 2021. PMID: 34631496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Aspects on the Plastic Nano- and Microparticles Toxicity in Zebrafish-Focus on the Correlation between Oxidative Stress Responses and Neurodevelopment.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 30;13(11):1810. doi: 10.3390/ani13111810. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37889690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicological effect and enzymatic disorder of non-studied emerging contaminants in Artemia salina model.Toxicol Rep. 2022 Jan 29;9:210-218. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.01.007. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36518451 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity Mitigation of Textile Dye Reactive Blue 4 by Hairy Roots of Helianthus annuus and Testing Its Effect in In Vivo Model Systems.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 25;2022:1958939. doi: 10.1155/2022/1958939. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35924274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Díaz-Cruz M.S., Llorca M., Barcelo D. Organic UV filters and their photodegradates, metabolites and disinfection by-products in the aquatic environment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008;27:873–887. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2008.08.012. - DOI
-
- Gao L., Yuan T., Wang W.H. Ecological risk assessment of organic UV filters in aquatic environment. J. Environ. Health. 2015;32:332–336.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

