Coenzyme Q10-Polyethylene Glycol Monostearate Nanoparticles: An Injectable Water-Soluble Formulation
- PMID: 31963934
- PMCID: PMC7023414
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9010086
Coenzyme Q10-Polyethylene Glycol Monostearate Nanoparticles: An Injectable Water-Soluble Formulation
Abstract
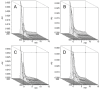
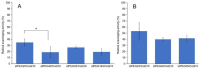
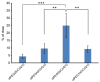
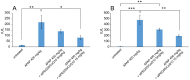
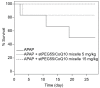
Therapeutic applications of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) are greatly limited by its lack of solubility in aqueous media. In this study, polyethylene glycol monostearate (stPEG) was used to construct micelles containing CoQ10 as a new formulation. The micellar formulations (stPEG/CoQ10) were prepared using five types of stPEG with 10, 25, 40, 55, and 140 PEG repeat units, respectively. The micellar preparation was simple, consisting of only stPEG and CoQ10. Next, we compared the physical properties and blood circulation of these micelles. The CoQ10 load of this formulation was approximately 15 w/w%. Based on the dynamic light scattering method, the average molecular size of the stPEG/CoQ10 micelles was approximately 15 to 60 nm. The zeta potentials of these micelles were approximately -10 to -25 mV. The micelles using stPEG25, 40, and 55 demonstrated high solubility in water. Furthermore, these micelles had in vitro antioxidant activity. On comparing the blood circulation of micelles using stPEG25, 40, 55, and 140, micelles using stPEG55 had a significantly higher circulation in blood. The stPEG55/CoQ10 micelle demonstrated a protective effect against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. In conclusion, these data indicate that the intravenous administration of the stPEG/CoQ10 micellar aqueous formulation is of great value against oxidant stress.
Keywords: coenzyme Q10; micellar formulation; oxidative stress; polyethylene glycol monostearate; water-soluble.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ubisol-Q10, a Nanomicellar and Water-Dispersible Formulation of Coenzyme-Q10 as a Potential Treatment for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 11;10(5):764. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050764. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34064983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Water-Soluble Nanomicellar Formulation Loaded with Trans-Resveratrol Using Polyethylene Glycol Monostearate for the Treatment of Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Nov 15;16(11):1462. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16111462. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39598585 Free PMC article.
-
Kolliphor® HS 15 Micelles for the Delivery of Coenzyme Q10: Preparation, Characterization, and Stability.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016 Jun;17(3):757-66. doi: 10.1208/s12249-015-0399-5. Epub 2015 Sep 4. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016. PMID: 26340950
-
PEGylated Solanesol for Oral Delivery of Coenzyme Q10.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Apr 26;65(16):3360-3367. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00165. Epub 2017 Apr 18. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28418660
-
Plasma coenzyme Q10 response to oral ingestion of coenzyme Q10 formulations.Mitochondrion. 2007 Jun;7 Suppl:S78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2007.03.003. Epub 2007 Mar 27. Mitochondrion. 2007. PMID: 17482886 Review.
Cited by
-
Coenzyme Q10 encapsulated in micelles ameliorates osteoarthritis by inhibiting inflammatory cell death.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 24;17(6):e0270351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270351. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35749420 Free PMC article.
-
Allyl Isothiocyanate Protects Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury via NRF2 Activation by Decreasing Spontaneous Degradation in Hepatocyte.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 23;12(11):3585. doi: 10.3390/nu12113585. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33238403 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidant Capacity and Bioavailability of Whey Protein Concentrate-Based Coenzyme Q10 Nanoparticles.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Dec 15;13(12):1535. doi: 10.3390/antiox13121535. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765863 Free PMC article.
-
Ubisol-Q10, a Nanomicellar and Water-Dispersible Formulation of Coenzyme-Q10 as a Potential Treatment for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 May 11;10(5):764. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050764. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34064983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Liver Fibrosis Theranostics.Front Chem. 2021 May 14;9:674786. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.674786. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34055744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

