Complete resolution of urinary incontinence with treatment improved the health-related quality of life of children with functional daytime urinary incontinence: a prospective study
- PMID: 31964382
- PMCID: PMC6975080
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-020-1270-2
Complete resolution of urinary incontinence with treatment improved the health-related quality of life of children with functional daytime urinary incontinence: a prospective study
Abstract
Background: To assess the health-related quality of life (HRQOL) of children with daytime urinary incontinence (DUI) based on pre- and post-treatment self-reports and parent proxy-reports.
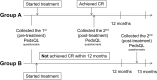
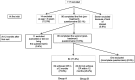
Methods: The study population comprised 117 children with at least one episode of DUI per week and their caregivers as well as 999 healthy children (control group). The Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory 4.0 (PedsQL) questionnaire was administered to assess the HRQOL of children. To assess the degree of improvement in HRQOL, we categorized children into two groups: group A achieved complete response (CR) to treatment within 12 months and group B did not achieve CR within 12 months. CR was defined as the complete resolution of symptoms or alleviation of symptoms to < 1 DUI episode/month.
Results: Valid responses were collected from 84 children [53 boys and 31 girls; mean age: 7.9 ± 1.5 years (range, 6-12)]. Sixty-two patients (73.8%) were classified into group A and 22 (26.1%) into group B. Based on self-reports, significant post-treatment improvement was observed in the scores of all PedsQL items (mean total score: 82.2 ± 11.3 vs. 87.2 ± 9.8; P = 0.003). Group A showed significant improvement in the scores of all PedsQL items after achievement of CR based on child self-reports; however, this was improvement not observed in group B.
Conclusions: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to demonstrate the complete resolution of DUI with treatment for improving the HRQOL of these children.
Keywords: Daytime urinary incontinence; Improvement; Quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does a serious game increase intrinsic motivation in children receiving urotherapy?J Pediatr Urol. 2019 Feb;15(1):36.e1-36.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Sep 19. J Pediatr Urol. 2019. PMID: 30401600
-
Health-related quality of life and treatment effects on children with functional incontinence, and their parents.J Pediatr Urol. 2014 Oct;10(5):922-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Mar 26. J Pediatr Urol. 2014. PMID: 24726201
-
Voiding school as a treatment for daytime incontinence or enuresis: Assessing the effectiveness of intervention by measuring changes in wetting episodes.J Pediatr Urol. 2018 Jun;14(3):256.e1-256.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2017.12.015. Epub 2018 Feb 5. J Pediatr Urol. 2018. PMID: 29452905
-
Adolescents with nocturnal enuresis and daytime urinary incontinence-How can pediatric and adult care be improved-ICI-RS 2015?Neurourol Urodyn. 2017 Apr;36(4):843-849. doi: 10.1002/nau.22997. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017. PMID: 28444706 Review.
-
Standard urotherapy as first-line intervention for daytime incontinence: a meta-analysis.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2018 Aug;27(8):949-964. doi: 10.1007/s00787-017-1051-6. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28948380 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative analysis of health-related quality of life between children with bladder and bowel dysfunction versus lower urinary tract dysfunction and healthy controls.Investig Clin Urol. 2024 Sep;65(5):494-500. doi: 10.4111/icu.20240137. Investig Clin Urol. 2024. PMID: 39249923 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical observation on the efficacy of Tongdu Tuina manipulation in the treatment of primary enuresis in children.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Jun 29;18(1):20230712. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0712. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 37398900 Free PMC article.
-
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders and Functional Urinary Disorders: A Fortuitous Association?Behav Sci (Basel). 2021 Jun 17;11(6):89. doi: 10.3390/bs11060089. Behav Sci (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204468 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austin Paul F., Bauer Stuart B., Bower Wendy, Chase Janet, Franco Israel, Hoebeke Piet, Rittig Søren, Vande Walle Johan, von Gontard Alexander, Wright Anne, Yang Stephen S., Nevéus Tryggve. The Standardization of Terminology of Lower Urinary Tract Function in Children and Adolescents: Update Report from the Standardization Committee of the International Children's Continence Society. Journal of Urology. 2014;191(6):1863. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.01.110. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources