Small-molecule targeted recruitment of a nuclease to cleave an oncogenic RNA in a mouse model of metastatic cancer
- PMID: 31964809
- PMCID: PMC7007575
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1914286117
Small-molecule targeted recruitment of a nuclease to cleave an oncogenic RNA in a mouse model of metastatic cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction to Supporting Information for Costales et al., Small-molecule targeted recruitment of a nuclease to cleave an oncogenic RNA in a mouse model of metastatic cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 May 3;119(18):e2204149119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2204149119. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35471914 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
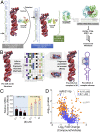
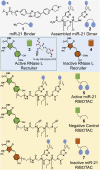
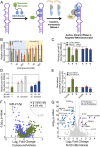
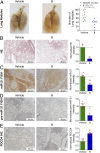
As the area of small molecules interacting with RNA advances, general routes to provide bioactive compounds are needed as ligands can bind RNA avidly to sites that will not affect function. Small-molecule targeted RNA degradation will thus provide a general route to affect RNA biology. A non-oligonucleotide-containing compound was designed from sequence to target the precursor to oncogenic microRNA-21 (pre-miR-21) for enzymatic destruction with selectivity that can exceed that for protein-targeted medicines. The compound specifically binds the target and contains a heterocycle that recruits and activates a ribonuclease to pre-miR-21 to substoichiometrically effect its cleavage and subsequently impede metastasis of breast cancer to lung in a mouse model. Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses demonstrate that the compound is potent and selective, specifically modulating oncogenic pathways. Thus, small molecules can be designed from sequence to have all of the functional repertoire of oligonucleotides, including inducing enzymatic degradation, and to selectively and potently modulate RNA function in vivo.
Keywords: RNA; cancer; chemical biology; metastatic; nucleic acids.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: M.D.D. is a founder of Expansion Therapeutics and M.D.D. and E.T.W. are consultants for Expansion Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Bartel D. P., MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

